Dukh-i-zhizniki
in America
An update of Molokans in America (Berokoff,
1969). —
IN-PROGRESS
Enhanced and edited
by Andrei Conovaloff, since 2013. Send comments to
Administrator @ Molokane. org
Chapter 2 — The First Years <Chapter
1 — Contents — Chapter 3> Updated: October 25, 2024
Contents
- Demens
Chose Los Angeles — 22 March 2025
- Bethlehem
District — Updated:
- Dr.
Rev. Dana W. Bartlett, Bethlehem Institutions —
Updated:
- Mystery
Woman, Land Donor Insulted — Updated:
- Bride-Selling
Scandal — Updated: 25 October 2024
- Mexico Colonies
— Updated: 26 October 2016
- Hawaii Colony
— Updated: 26 October 2016
- Folk
Medicine — Updated:
- Weddings
— Updated:
- Funerals —
Updated: 29 February 2020
1. Demens Chose
Los Angeles
 PAGE 32 The city of
Los Angeles was chosen, instead
of Canada, for
PAGE 32 The city of
Los Angeles was chosen, instead
of Canada, for by these Spiritual Christians from Russia Molokans by P. A. Demens* as for
their haven because was
in many respects it was ideal for
their purpose though they may not have been aware of the fact at
the time. Los Angeles in those days (1904+)
was not the overcrowded, smog ridden** city it is today
was in 1969 when Berokoff published his
book. Indeed, by present day standards it could not be
called a city but a pleasant,***
quiet, overgrown smokey town with
a population of 102,000 according to the census of 1900. It was
a center of a fertile agricultural district****
populated mostly by white Protestant
elderly people seeking health or a comfortable place of
retirement in a healthy, mild climate as
advertised.
* J.K. Berokoff oddly never mentioned P. A Demens (photo), who
diverted them all from Canada to avoid the fate of the Dukhobortsy
there, to the City of Los Angeles, and falsely recast this
"Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians" from Russia into a
simple single unique word, "Molokans" (dairy eaters). When
Pytr Dementsev arrived in America he simplified his surname
to Peter Demens. He probably re-branded the immigrants with
this very easy-to-pronounce word to simplify their
introduction to Americans as ideal White Protestant
settlers, hard workers, non-drinkers, non-smokers, not
indigent, etc. Few were Molokane, who mostly moved
to San Francisco in 1906. The non-Molokane were a
diverse mixture of about 25 different congregations, much
too complicated for him to quickly explain or understand. In
1910, after many interviews he published in Russian his
analysis of the failure in 1906 of the "Molokan Agricultural
Colony" in Hawai'i. (To be posted)
For 30 years, since his arrival to the
U.S. in the 1880s, this
Russian-born tycoon, Pyotr Alekseyevitch Dementyev (Пётр
Алексеевич Дементьев), recast himself as Peter A.
Demens and became a prominent citizen and businessman.
He recommended in numerous article published in Russia that
all Russian immigrants to North America would come to Los
Angeles first. For many immigrants from Russia with little
money, he personally arranged for their travel to Los
Angeles from their American immigration
port of entry, got them jobs in businesses he either owned
or had co-owned — a lumber yard, planing mill, soap factory,
and commercial laundry in Los Angeles; his citrus farm in
Alta Loma; and, with his friends. He also helped the
immigrants, who did not want to live in the city, negotiate
farm colonies in Hawaii, Mexico and California; and explore
many other settlement sites in North America by introducing
the immigrant scouts to railroad land agents.
** "Industrial smoke and fumes were so thick during one day
in [January]
1903 that residents mistook it for an eclipse of the sun.
From 1905 to 1912, the Los Angeles City Council adopted
several measures to combat dense smoke emissions." — "The
Arrival of Air Pollution : The Southland's War on
Smog: Fifty Years of Progress Toward Clean Air (through May
1997"), South Coast Air Quality Management District, Los
Angeles.
Street
dust and mud were a widespread nuisance.
*** The Bethlehem and Flat(s)
districts smelled of factory smoke and asphalt oil, methane
from natural gas storage tanks, and horse shit, with flies,
rats and ground squirrels. Many streets were dirt dusty,
rutted from wagons in mud, and occasionally oiled.
**** Around 1900, Riverside county was
the most productive agriculture county of California.
Few, if any, immigrants came here directly from their port of
entry. Although there were many some
foreign-born speaking
immigrants here when the first Spiritual
Christians Molokans arrived from
Russia, mostly Jews and Italians seemed
to live closest to us in the Bethlehem district.
English (11K), German (11K), and
Canadian (10K, mostly English). Later Jews
(Hebrews, 10K), Mexicans (35K), Germans
(11K), Russians (7.5K), Japanese (7.5K),
Croatians (7.5K), and
Italians (6.5K) arrived about the same
time as the Spiritual Christians from Russia. Excluding
Mexicans, Japanese and Chinese, many may have indirectly come
to Los Angeles These came after
spending some time in the cities of the Eastern seaboard or Canada, and having heard of the
wonderful climate advertised in
Southern California, its roomy new towns and cities, fled the
crowded tenements of the East and remained here permanently.
In 1902
"Influx of Indigents ... The New Hospital Building Will
Encourage Them ... Cost Will Be $3500 Per Bed ... A Million to
Be Spent in Next Ten Years," Los Angeles Herald,
Settlement Houses (added
Sept 23, 2020; updated May 28, 2023.)
Immigrants had a
3-year probation to be productive or be deported. Many
wealthy people created charities to help them stay, like settlement
houses, the early form of today's social
service organizations and agencies. The main difference
is that the providers lived in the settlement house which was
funded by private donors, decades before the government
sponsored social support programs for the needy.
Several American
churches had "foreign missions" and "home missions".
Presbyterian foreign missionaries met and documented a new
tribe of Molokane in Novorossiaya (New Russia), Tavria
oblast, (South Ukraine) in
In 1894 the Los Angeles Settlement
Association (LASA) was founded. "The settlement house movement
sought to help migrant and immigrant families to adjust to
their new surroundings by offering a community space, social
events, education, food, and shelter. By
1911, there were six settlement houses operating in Los
Angeles, four of them with religious affiliations and
two secular (non-religious). Many of the settlement house
workers tended to be educated women from upper or middle class
backgrounds. (Judith Raftery, Land of Fair Promise:
Politics and Reform in Los Angeles Schools, 1885-1941,
Stanford: Stanford University Press, 1992, page 19 ; Woods,
Robert Archey; Kennedy, Albert Joseph, eds. Handbook
of Settlements. Charities Publication Committee,
New York, The Russel Sage
Foundation,
1911, page vi.)
- Bethlehem
Institutions, 510 N. Vignes (at Ducommun), founded in
1887 by the First Congregational Church as the Sainsevain
Mission, on Sainsevain street (changed to Commercial street)
at Vignes (1 street south). It served as a free day-care and
Sunday school. In 1892 it was renamed and moved in 1892 to
the corner of Vignes and Ducommun streets. In 1896
supervisor Rev. Dr. Dana Bartlett was hired. Served 9
nationalities. Supported 17 girls' clubs, and about 400 kids
per month. At least 900 kids lived in the neighborhood.
- Los Angeles Settlement House, 402
Bauchet, founded by Rotary Club of Los Angeles, supervisor:
Ruth C. Hoffman (photos).
Pamphlet: "The
Los Angeles Settlement House : dedicated to the
Americanization of our alien population," 1910-1925, 4
pages.
- Brownson
Settlement House, 711 Jackson, founded by Diocese of
Monterey and Los Angeles of the Roman Catholic Church, built
1905, administered by the Bureau of Catholic Charities (history,
photos) Serves 9 nationalities, 90% Mexican.
- Santa Rita Settlement House, Buena
Vista st, administered by the Bureau of Catholic Charities (history,
photos)
- Los
Angeles College Settlement House, founded in 1904 by
LASA, 4th location at 428 Alpine st (at Castellar). Purpose:
Americanizing aliens. Closed 1910?
- Moses Mendelssohn Settlement House for
Girls, 738 Turner, (renamed "Ida Strauss Day Nursery" and
moved to 531 N. Boylston St.)
- King's Daughters Day Nursery, 134
N.Clarence street
- St Elizabeth's Day Nursery 135 North
Anderson street
- Y.W.C.A. International Institute,
Boyle ave,
- Neighborhood Settlement House,
Reach: 600 to 700 families.
- Pacifist-Socialist Fanny Bixby worked
with neighborhood Russian kids from her house in Karakala
and funded many social programs.
Major Immigrant Nationalities in Los
Angeles by 1915
Mexican
|
35,000
|
||||||||||
|||||||||| |||||||||| |||||
|
English
|
20,000
|
||||||||||
|||||||||| + Canadian English
|
German
|
11,000
|
|||||||||| | |
Hebrew
|
10,000
|
|||||||||| many Jews from Russia
|
Russian
|
7,500
|
||||||||
Orthodox + non-Orthodox
|
Japanese
|
7,500
|
||||||||
|
Croatians
|
7,500
|
|||||||| |
Italians
|
6,500
|
||||||| |
Though people of color (non-whites) were a
large fraction of the population, advertisements for Los Angeles
promoted it as the "White Spot of America" — propaganda to
attract more white residents. "In 1920-21, the U.S. Chamber of
Commerce created maps designating business conditions around the
country — areas shaded black were
“bad,” grey was “fair,” and white was “good.” On this map, LA
was literally a “white spot” among areas shaded in black and
grey, leading Harry
Chandler to dub Los Angeles as “The White Spot of
America.” The term caught on and by 1924 the phrase “Keep the
White Spot White” was used throughout the city." (Hollywoodland,
Finding Los Angles, blog by Rachel
Kafka and Nate Hennagin, January 7, 2019.)
Map of the Foreign-Born Population of the United States, 1900
A Spotlight on a Primary Source by Henry Gannett, The Gilder
Lehrman Institute of American History.
https://www.gilderlehrman.org/history-resources/spotlight-primary-source/map-foreign-born-population-united-states-1900
Immigration to the U.S. in the Late 1800s : Map of immigration
to the U.S. from the east and west, National Geographic Society
https://www.nationalgeographic.org/photo/immigration-1870-1900/
Naturalization Act of 1906
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Naturalization_Act_of_1906
Bolger, E. (2013). Background history of the United States
naturalization process. Retrieved from
https://socialwelfare.library.vcu.edu/federal/naturalization-process-in-u-s-early-history/

Source: "Immigration
Education Leaflet No. 1," Annual Report of the Commission of
Immigration and Housing of California, Volume 2, 2 January 1916, page 125.
Eugenics
was a new "scientific" policy adopted in California to justify
racism (White
supremacy) and for
population control. Preference was given to white, protestant
eastern and southern Europeans. People of color and
non-protestant faiths were not preferred, and many White
elites feared that Jews and colored people could intermarry
with the Whites.
The politically correct and preferred
immigrants were white
Protestants from north-western Europe. Fortunately, the
Spiritual Christians from Russia met 2 of these 3 preferred
requirements — white (some blond, blue eyed), and protestant.
The probable advice given by the first Russian hosts in Los
Angeles (de Blumenthals, Cherbak, Demens) for
those planning to stay in Los Angeles, was to quickly learn to
mimic the north-western
European immigrants in America in dress, behavior,
education and speech. Those who wished maintain their peasant
Russianess should move to farms.
Note that the "Estimate of Foreign Born"
table above is divided into European (most desirable) and
Non-European (least desirable, colored); and the Europeans are
divided into Slavic (less desirable) than the Non-Slavic.
Earlier immigration was mostly White northern Europeans — the superior Nordic race.
The Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians from Russia were
classified among the moderately desirable upon arrival, but
Demens did his best to present them as the "most desirable"
future best citizens, as white Protestant non-drinkers,
non-smokers, strong, honest and economical workers.
Demens had traveled extensively and
testified to anyone who would listen that life in Southern
California is the greatest. He enjoys the mild year-round
outdoor working climate, new water for rural and urban use,
new trade via the Panama Canal, railroads to ship his citrus — and Southern
California businesses launched a huge advertising campaign to
lure "white" investors and "white" workers to their "White
Spot" to compete with San Francisco. These geo-economic
factors earlier diverted the Demens
family from continuing their original move to San Francisco in
the 1890s after they stopped in Los Angeles. Demens protested
the Dukhobor move to Canada, and published many articles in
Russian journals promoting life in the United States,
especially Southern California.
But the Spiritual Christians from Russia
Molokans,
profiting from the two year experience of the Agaltsoff group,
were spared these needless trials when most
they came directly to Los Angeles lured by Demens. Had they by some
unfortunate mischance landed in New York, Boston or Philadelphia
as hundreds of thousands of other immigrants did and were per
force compelled to live in the crowded, unheated, rat-infested
slums of those cities, they would have abandoned their place of
refuge and fled headlong back to their village homes in Russia as fast as they were able to
save enough money to do so because such living conditions were
simply not for them.
Berokoff obviously did not know that they
were destined for Canada because he describes what could have
happened if they stayed in the United States, and it was the Agalstoff,
Halopoff, and Slivkov scouts and the prophet E.G.
Klubnikin who led them to Los Angeles, but only as a temporary
refuge.
In contrast, in research begun 5 years
after Berokoff's book and published in 1978, the Maksimist
William Wm. Prohoroff III ("Billy Pro"), who helped lead
the migration (pokhod) to Australia in the 1960s but
returned in the 1970s, claimed Demens (misspelled as
Demonsoff) " ... whose name explains his mission [i.e.;
demonic]. Therefore the dollar brought our people to Los
Angeles and not the Holy Spirit." Prohoroff concluded that
Canada was the correct prophetic land of refuge for
Rudomyokin's followers, not Los Angeles. Prohoroff only
mentioned Demonsoff(sic) twice. (Prohoroff, William. Maxcim
Gavilovich Rudometkin "King Of Spirits" : Leader of New
Israel (Molokans), Image Printing, Sacramento, CA. 1978,
pages 353+, 361-362.)
In the first place they could not have endured life in a
tenement house where dozens of families of all nationalities PAGE 33 lived together.
Secondly, it was a positive necessity for them to have a place
of worship isolated from crowds of non-Spiritual
Christians Molokans (ne nashi). It would have been
utterly impossible for them to conduct their worship, their
holiday feasts, their wedding or funeral ceremonies in the
prescribed manner. It would also have been impossible for them
to conduct prayer services in their own homes as they were
accustomed to do because other dwellers of the multi-familied
tenements would have forced them to give up the custom. Not so.
Many of the first Spiritual Christians
from Russia lived in cramped conditions with outsiders (ne nashi) "of
all nationalities" and races as neighbors in the slums of Los
Angeles. Many first lived in horse barns (garages) and small
dirt-floor shacks built from scrap materials, somewhat similar to
their former houses in Russia, and some worse. One
of the worst neighborhood slums was called "Ficket hallow"
at the bottom of a wash bed along south
Ficket street south of Stevenson blvd. (renamed
Whittier Blvd. in 1923) See map of Karakala below. My mother's
cousin, Fred Wm. Shubin told me that their house in this
neighborhood had a "dirt floor with no foundation" — just
a wood shack built on the ground. I got to know Fred well
when he and his brother/ contractor W. A. Shubin helped
found the Heritage Club in the 1980s. They developed Shubin
Lane, Whittier, CA , one-third mile of new homes
built along an abandoned railroad track.
This was the first climate these
immigrants ever lived in with no winter snow. Many tenements
and cooperative housing in large eastern cities had community
rooms which would have provided space for assembly until they
bought or rented their own meeting halls, as did similar
immigrant groups in those cities. Many large American cities
had more settlement houses and immigrant aid societies, better
than in Los Angeles, and a lot of farmland was for sale by
railroads, and sugar factories needed farmers. But Demens
apparently was very persistent to bring most all to Los
Angeles, away from Canada which was their original
destination. He did not object to anyone wanting to leave Los
Angles, and personally helped negotiate the failed migration
to Hawai'i. In 1910 he published an analysis in Russian as to
why the Molokan Agricultural Colony in Hawai'i failed.
(In-progress)
On the other hand, Los Angeles, being a new city with no
natural obstacles to expansion, was able to spread itself,
allowing space between houses as well as front and back yards
for the use of each occupant. Its houses too, were relatively
newer with individual plumbing and in some cases, wired for
electricity, which was not the case in the East. Many older houses used gas lights. All
these things combined, permitted the Spiritual
Christians
Molokans the
environment to practice their religions
undisturbed. Not so.
In 1883, Los Angeles was the first city
in the USA to entirely abandon gas for street lighting and
replace it with electricity. There were 242 electric lamps
with a circuit length of 85 miles. By 1889, the Los Angeles
Electric Company had 235 customers, and many stores their own
street lights. Downtown Los
Angeles had street lights at night. Before these Russian
arrived, the Flats were lit by a large very high arc lamp. ("Electricity
in Early Los Angeles," Water and Power Associates.)
.
While most of the East settled by immigrants was electrified
by the end of the 1920s, the map below shows that California
ranked third in the country, getting electricity sooner
than most cities.
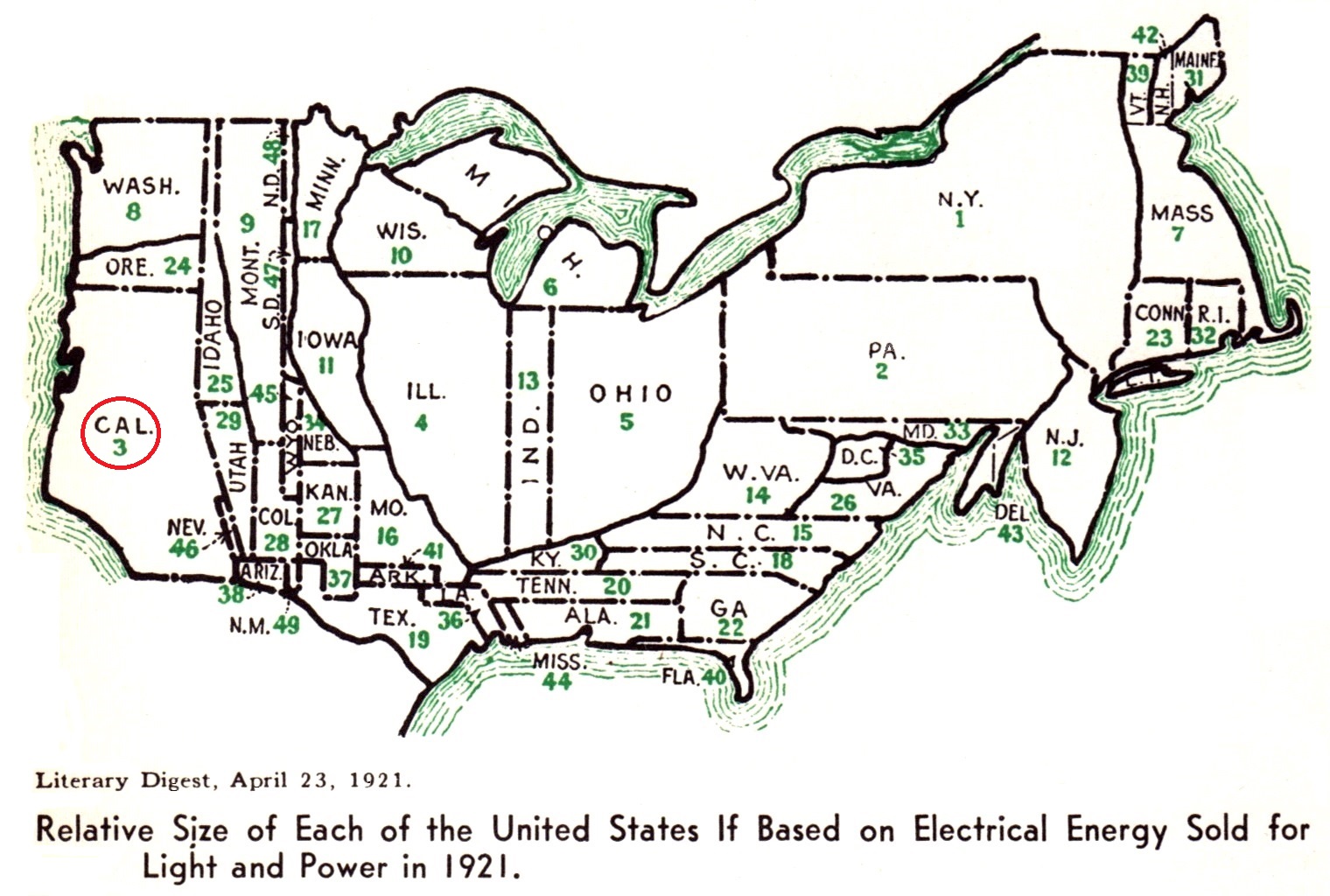
From: Madrigal, Alexis
C. "A
Map of American Electricity Use in 1921. Power was not
evenly distributed." The Atlantic, July 26,
2013.
Original: "Rank
of States as Users of Electrical Energy" (3 maps) with
article: "Electrical
Importance of the Various States : Map Indicates that
Almost 80 per Cent of the Electric Light and Power
Industrial Field Lies East of the Rocky Mountains [with 92%
of population and 61% of land area] ... ", Electrical
World, March 19, 1921, pages 650-651.
Also: "Electrical
Rank of States," Literary Digest, April
23, 1921, page 21; and Welter, Ben. "An
electrifying infographic," Blog, Star Tribune
blog from archives, Minneapolis, MN, Feb. 27, 1921. Image
saved at Archive.org.
The new houses with plumbing that
Berokoff mentions was due to an extensive slum rehab program
conducted on the east-side of downtown Los Angeles, from the
Mexican quarter (Olvera Street area), through Chinatown, to
the Flat(s). The goal was to reduce vice (prostitution,
gambling, drugs, theft, drunkenness, juvenile delinquency,
etc.). In 1907, Los Angeles City began to fine slum landlords
if they did not eliminating their "cholo
courts" — several shack houses on a lot with
a single outdoor water faucet and outhouses. Many of the targeted
properties were along Utah street and visible from
the streetcar lines extending to the new subdivisions farther
from downtown.
By 1913 the Rev. Dr. Dana W. Bartlett was
appointed by California Governor the head of the
California Immigration Commission
Land speculators were selling property
lots to developers, and contractors were building houses along
the electric street car tracts farther from downtown which
provided jobs for skilled immigrants. My mother's grandfather,
Ivan Vedenoff, was a carpenter on
at least one house on Anderson street along the Los Angeles
River, which was pointed out to me by my grandmother Sasha
(Vedenoff) Shubin in the 1960s.
Several police reports were filed, and
large hearings held about the noisy "Russian Holy Jumpers"
disturbing the peace. Much effort was expended to move the
most resistant to city life out of Los Angeles to any rural
area, including Mexico and South America. At least a dozen
land agents approached them, some on behalf of tycoons
offering large tracts of land.
After three years or so in Los Angeles, the more enterprising
ones were able to purchase their own homes.*
These immediately proceeded to install in their back yards the
typically Russian institution, the "bania"
(Russian: steam bath house),
which, for a fee of ten cents were utilized by those who did not
possess such a luxury. One enterprising
Armenian Prygun family built a large family-size banya
in their backyard which they rented by the hour (@ 10
cents). They got free wood from Armenian rubbish wagon drivers
who tossed it over the back alley fence, which saved the
driver from taking it to the city dump and incinerator.
It was not very long before other families also bad the added
luxury of a home-made brick bake oven in their back yards where
delicious bread was made by the enterprising housewives. Many in
cramped houses cooked outdoors on fire (wood and kerosene),
which injured people and burned a few houses. The air was
polluted with smoke from home incinerators and businesses,
and all city rubbish was burned in the city
incinerator on Santa Fe Ave outside the city limits in
today's Vernon. Home incinerators were banned in 1957, which
increased curb-side recycling, which was stopped in 1961.
until the was the law until Sam Yorty was elected mayor due
to his campaign promise to abandon recycling.
*
In 1918, Sokoloff estimated that
about 1 of 200 heads-of-household had applied for
citizenship, less than 1%.
Although during the first years the Spiritual
Christians Molokan families made the utmost use of
each house by crowding each bedroom, there was, nevertheless,
some houses where a large room was made available for the
community as an assembly (meeting) house
(собрания : sobraniya) a church
and since the houses on either side were usually occupied by Spiritual Christian Molokan
families, there was no disruptive interference from neighbors
or from hoodlums.
Berokoff may have wrote "hoodlums" due to
these kinds of stories:
- In September 1906 an angry gang of
union strikers from San Pedro took the train north to the Bethlehem
district (west of the Los Angeles River) to threaten a
Russian meeting (sobraniya) in progress,
warning the Russian men to stop working as strikebreakers.
("Make
Threats With Prayers: Union Roughs of San Pedro Invade
Meeting; Try Bulldozing Tactics With Russian Congregation;
Molakanes at Worship Repel Totemite Demands." Los
Angeles Times, September 3, 1906, page I-15. — 300 at
prayer meeting at Stimson Lafayette School, headquarters of
the Russian colony. ... Union thugs from San Pedro told
Russians not to resume work in lumber yards in San Pedro....
83 [Spiritual Christians from Russia]
Molokane
employed at San Pedro since strike, at $2.85/day.)
- Elder men with long beards were often
heckled on the streets in the Flats and called "whiskers",
even by streetcar drivers, when they announce the Salt Lake
Station stop on First Street entering the Flats.
- About 1967, I
witnessed a young (~8-10 years old) ethnic "Mexican" boy
born in Boyle Heights, Los Angeles, on Eagle street (1/2
block east of Lorena st., 1 street south of 4th street)
harass my grand-mother's neighbor, the elder Adnoff, by
reaching through his car window to pull on his long beard
while he was driving on the street. The kid later
bragged
Private congregation meeting halls were
not likely until the 1920s due to a series of culturally
disruptive events which removed thousands from the Bethlehem
district of Los Angeles, and a decade later
replanted most back to a more accommodating rapidly growing
suburban metropolis east of the Los Angeles River called "The
Flats":
- 1905 — Los Angeles — More than 100 move to the
Guadalupe
Valley, Baja California, Mexico.
- 1905 — Los
Angeles — Over 400 sign up to move to Hawaii. Land is
scouted by Demens, Shubin, and Slivkoff.
- 1906 Jan-Aug — Hawaii
colonies start and fail. Returning Molokane and a
few Pryguny stay in San Francisco. Most Pryguny
and other zealots, with some Molokane, return to
Los Angeles.
- 1907 — Los Angeles urban renewal.
Cleaning up "cholo
courts", many on on Utah Street, forced 2000+
Mexicans out, and many Russians into new housing.
- 1907-1910 — More move to Mexico
settling in 2 rural areas north of Ensenada —
LA Mission and San Antonio.
- 1909 — Los Angeles Housing code
enforcement.
- 1910 — Los Angeles — Rejection of a
grand resettlement of Spiritual Christian villages arranged
by Cherbak to land "near Santa Barbara"
- 1911-1915 — "Bride-selling"
scandal.
- 1911 October — Arizona first
colony (Darachak) goes to land west of Glendale, Arizona
- 1912-1915 —
From Arizona, Pivovaroff traveled to Los
Angeles and San Francisco to invite more to come to Arizona.
- 1912-1916 — Arizona — At least 4
congregations move to adjacent land in Arizona — Darachak,
Novo-Selim, Bichnak, Tiukma (Jeromskiy).
- 1913 — Los Angeles Aqueduct (Owens
Valley aqueduct) begins to deliver water.
- 1914 — Los Angeles — Closure of
the Bethlehem Institutions for poor management and
accounting; Americanization
Day begins
- 1915 —
Los Angeles — 2 Spiritual Christian Maksimist books
published: songbook, and collection of M.G. Rudomyotkin
writings. Flag
Day begins
- 1915 — Los Angeles — Home Teachers
Act; Lillian
Sokoloff study begins.
- 1916 — Arizona — Resettlement of
Novo-Mikhailevka congregation from Mexico to Jerome
Junction, Arizona, then south to join 3 other
colonies, forming a large settlement area about 7 miles long
and 1-2 miles wide with 4 separate congregations.
- 1917 — Arizona — World War I; 34 in
Arizona jailed for 1 year (served 10 months); and 6
imprisoned for 4 years for not signing anything.
- 1918 —
Los Angeles — Sokoloff study
published
- 1920s — Los Angeles —
Post-war recession, mass migration back to Los Angeles
Flat(s) and Karakala districts.
- 1923 — Los Angeles
— Pauline Young enters Department of Sociology,
University of Southern California; assigned to study
non-Orthodox immigrants from Russia.
- 1926 — Los Angeles — Young's masters
thesis.
- 1928 — Los Angeles
— Final version of Kniga solntse, dukh
i zhizn' (Book of the Sun, Spirit and Life),
published.
- 1929 — Los Angeles — Young's
doctoral (Ph.D.) thesis.
- 1932 — Los
Angeles — Young's book: The Pilgrims Of
Russian-town: Обшество Духовеныхъ Христиiанъ
Прыгуновъ въ Америкѣ: The Community of
Spiritual Christian Jumpers in America : The
Struggles of a Primitive Religious Society
To Maintain Itself in an Urban Environment.
By 1916, few, if any Spiritual Christians
from Russia attended Amelia Street School, Bethlehem district,
indicating most moved east of the Los Angeles River to the
Flat(s). (Chase, Amanda Andrews. "Report
of A Home Teacher," Commission of Immigration and
Housing, in Annual Report of the Commission of Immigration
and Housing of California, Volume 2, 2 January 1916,
page 139.)
The inter-urban migration of Spiritual
Christians from Russia eastward across the Los Angeles River,
probably oriented these people to continue east across Los
Angeles County for the next century. They aimed east in steps.
Probably due to poverty and the
need for group support by familiar people (relatives, fellow
villagers), a "follow-the leader"
shifted those from Russia southward into the Flat(s), mainly
between First and Fourth streets. This path could have slotted
them eastward along a radial projectory from the city center
to their low-class
residential sector that continues today, along
a ray from Los Angeles city center, through the Flat(s),
Karakala, Boyle Heights, East LA, Montebello, Pico Rivera, and
Whittier. The Jews developed their businesses along Brooklyn
Ave north side, while Japanese tracked in-between, mainly
along First street. In later decades the Jews would abandon
Boyle Heights for the west side of Los Angeles; and, the
Japanese, having lost their property during WWII internment,
would maintain a strong Downtown to Boyle Heights presence
along First street and Second streets but scatter to find new
housing. The more rapid assimilation of "other" White groups
who left Boyle Heights allowed the Spiritual Christians
from Russia in the city to fully integrate among Mexicans
(Hispanics) and Japanese which allowed them to maintain their
separate foreign Russian culture probably longer than if they
were concentrated in a White (Caucasian) area.
The section of the city where the Spiritual Christians Molokans first settled was in a close
proximity to all their needs. Lumber yards, cold PAGE 34 storage plants
and the rail road yards where work was to be found were all
within walking distance. The downtown shopping district was not
more than half mile away.
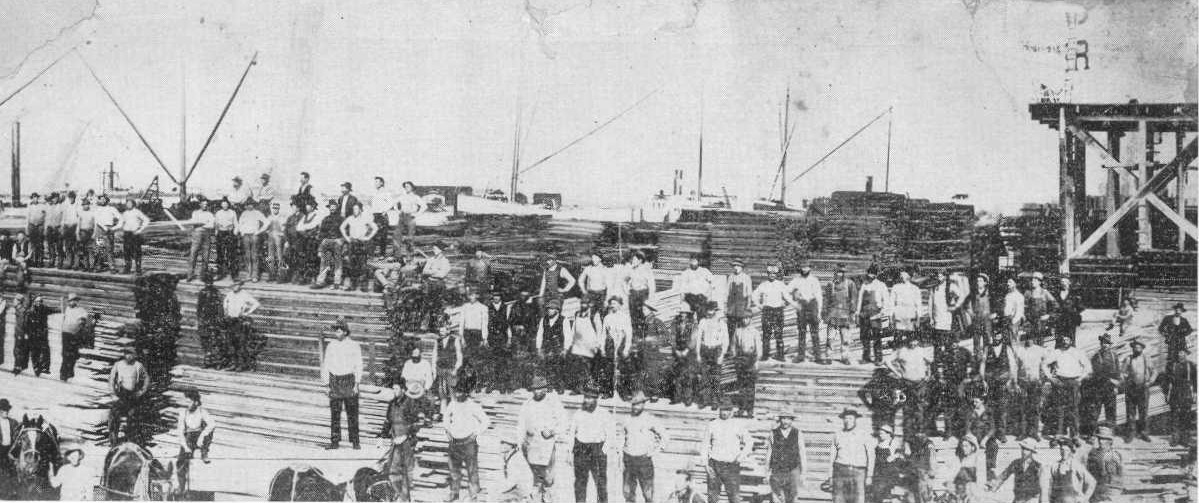
The
first 6 families arrived in Los
Angeles about May 1904. They were led by
Vassili Gavrilovitch Pivovaroff and financially
assisted by P. A. Demens. They called their united faiths
the "Brotherhood
of Spiritual
Christians," and settled east of the Los Angeles River
on Utah Street, north of 1st Street, near Utah Street School.
There are no reports of more arrivals until about 7 months
later in January 1905. Many of the 1905 arrivals settled in
the Bethlehem district, which was closest to the main train
station and the Bethlehem Institutions where they got
extensive free help in the Russian language, many free
services and free use of facilities. During the first decade,
many lived in small crowded wood shacks, some with dirt floors
and outhouses, some in horse barns, for the cheapest rent. It
was a huge cultural shock for people who lived in rural
villages. Upon arrival, they saw street lights at night, tall
buildings, electric street cars, a long bridge that separated
the 2 clusters of their Brotherhood. They lived next to and
walked among many nationalities and cultures —
Japanese, Blacks, Jews, Italians, Slaves, Mexicans, etc.

|
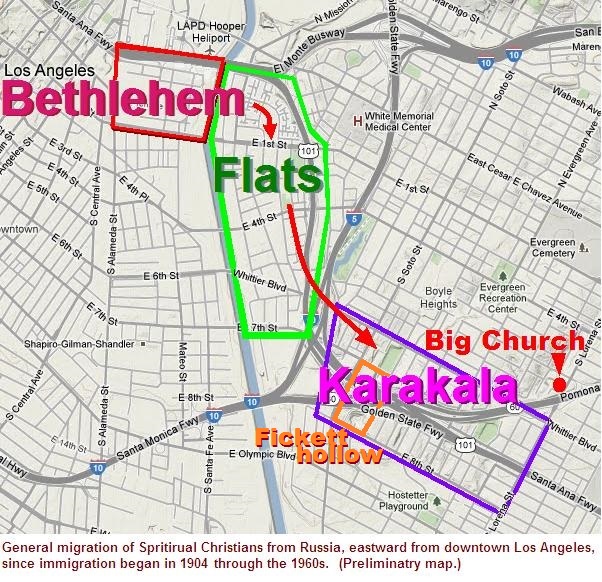 |
2.
Bethlehem district

The Bethlehem
district mapped above was bounded
on the west by Alameda street, on the East by the river bed, on
the South by East First Street and on the North by Aliso Street.
The label "Bethlehem district" was
created for this history of Dukh-i-zhizniki in America
because it was needed to identify this unique Los Angeles
immigrant neighborhood that is often referred to, but was
never officially named nor outlined in any publication. Up to
1909 the most common label was the "8th
Ward." Now, and in recent
decades, it is sometimes associated with, or part of, what is
variously called the Arts
District and East
of Alameda. Historically, reporters
often referred to a "foreign
district / quarter" of which this was a part, but which
shifted in time by immigrant group and by reporter. This
Bethlehem district was part of the 8th Ward, in an area often
called the "wholesale/
warehouse district." In 1909 Marco Hellman (son of
banker Isaias
W. Hellman) promoted a "commercial district" on the east side
of Alameda, through and across the Bethlehem
Institutions, to the Los Angeles River, to help destroy
at least 9 of the of the 21+
residential units used for prostitution in the
"red light" area. In the early
1900s the 8th Ward was the most blighted over-crowed
industrial and commercial area with shanty shacks, the most
bars, and the most prostitutes. Many of the incoming
discriminated immigrants (Jewish, Japanese, Slavic) lived in
garage horse barns with dirt
floors and they cooked outdoors.
Many rented a shack in "slums" and "courts" where renters
shared a common water faucet, outdoor bath and outhouses. As
many as 10 people would share a 10'x10' room (100 sq. feet,
size of a small one-car garage).
Housing Commission, 1906-1913
In 1903 a city Housing Commission was
proposed, but not formed until 1906, to survey and recommend
demolition of slums and solicit investors to build affordable
new housing with indoor plumbing. Even the women's clubs were
asked to build housing and a maternity hospital for the poor.
During its 5 years, the Commission produce 3 reports from
February 1906 to 1913.
The board and support staff consisted of men and women, least
one medical doctor, architect, several building inspectors,
social workers, and an advocate for the poor (Rev. Dana Bartlett).
The Commission had no regulatory
power, but worked with the Board of Public Works and the
Health Commissioner. The social
workers tried to teach residents how to live healthy, and the
inspectors advised owners of building code violations. Many
buildings were demolished near the Plaza and replaced with
acceptable housing. East of the river, the Flat(s) and Boyle
Heights had more vacant land to develop in compliance with the
new codes. In 5 years the Commission improved housing for about
10,000 inhabitants, and it projected 100,000
foreigners per year when the Panama
Canal will be finished in 1915.
February
"The Russians are
gregarious and have formed a "Little Russia" covering an
area of 15 to 20 square blocks. It has been estimated that
there are 10,000 Russians in the city, many of whom own
their own homes." (1913, pp.
20-22)
"There are ... 33
nationalities ... The majority of them are Mexicans,
Russians, Italians, Slavonians and Austrians.
"The Russians ...
are employed in the lumber yards and seem to have almost a
monopoly of this work and receive from $2.00 to $2.50 per
day. But among the Russians are some carpenters,
plasterers and plumbers. Some Russians own their own
[horse and wagon] teams and do heavy hauling. The Russian
women find employment in the laundries and during the
summer in canneries." (1913, p.
24)
Los
Angeles in 1905 when Spiritual Christians Arrived from
Russia.

Bridges built across the Los Angles River to extend streetcar
service eastward to new sub-divisions caused many Bethlehem
residents to also move eastward across the L. A. River into
the alluvial
river Flat(s) in the 9th Ward, followed by social
services (Y.W.C.A. International Institute, Volunteers of
America, Maternity
Cottage, city parks, etc.)
Bethlehem Timeline, 1892-1908
The
Bethlehem Institutions (1892-1914) were a complex of
buildings dedicated to provide every service
needed by the homeless, the working poor, and to assist
immigrants with food,
baths, housing, medical, citizenship and language education,
legal guidance, counseling, clothing, furniture, job training
and placement, meeting places, etc. It was a social support
structure to uplift the poor, the "submerged
tenth" of the population.
- 1892
— The First
Congregational Church of Los Angeles
opened an outreach mission-church named
"Bethlehem," nicknamed "headquarters" and the
"Mother Church," marked on map above at the NE corner of 510 N. Vignes
and Ducommun streets. Other faiths also had missions
in this district.
- 1896
— Bartletts moved
to Los Angeles to be assigned as missionaries at the
Bethlehem Institutional Church.
- 1901
— A public bath house,
laundry and plunge (swimming pool) was built, south
across Ducommun street. In the
winter, a wood floor covered the plunge and the room was
used to train people how to recycle, similar to Goodwill
Industries. Scavenged and donated items were
restored and mostly given to the needy while workers
learned a trade and some English. This program may have
introduced some Spiritual Christian families to work
in recycling and rubbish collection in Los Angeles.
In Russia the pacifist Spiritual
Christian men recruited to the military
who refused to carry arms were "distributed
among the sanitary and transport corps," which
trades they probably continued in Los Angeles.
- 1902
— Bethlehem Institute of Social Study started by Bartlett
and grew as an annual week-long residential program of
intense college sociology lectures and visits to welfare
and legal agencies serving the poor. After 1905, students
were guests at Spiritual Christian meetings (sobranie)
during their field studies.
- 1904
— Purchased or donated a 52-room, 2-story single Men's
Hotel. Built as the Ducommun family house, then used as a
dormitory for News Boys, about 100 feet west of the Mother
Church.
- 1905
— Rev. Bartlett assigned manager-superintendent of
Stimson-Lafayette Industrial School, 1 block from
Bethlehem Institution, on Lafayette street. The building
was built as a residential women's trade school by Mrs.
Stimpson, then converted to a school and community hall
primarily used by Spiritual Christians from Russia. The
first Russian-speaking preacher/minister was Rev. Henry
Teichrieb who served to 1910.
- 1907 — The
Russian Economical Association Company (R.E.A.C.) was formed
in January 1907 to own and manage a co-operative (communal)
store and bakery at 209 N. Vignes, at the southwest corner
of Banning street. The manager was paid $11/week and every
clerk was a limited stockholder. It failed in 1908 due to
mismanagement and a suit by one man for back wages. This was
the first and only Russian cooperatvie
store.
- 1907 — A women's charity hospital is
planned for the Russian and Cholo (Mexican) district.
- 1908
— Japanese congregation invited to share
"Mother Church". Most Spiritual Christian faiths
apparently preferred to share the larger
Stimson-Lafayette Industrial School with easy to move
tables, benches and chairs; a kitchen and court-yard.
Immigrating
waves of Spiritual Christians from Russia of all
faiths were invited to the "Mother
Church" where staff fed them, showed them to the
bath house and laundry across the street, let them sleep
anywhere, allowed them to use the halls for meetings
(sobranie), helped find jobs and housing,
orientated them to the local surroundings and city life
in regular group counseling classes. The Bethlehem
Institutes could temporarily house and feed up to 300
people in an emergency.
For 6 weeks in February and March 1905,
2000 American Christians marched, played music and sang daily
through Los Angeles slums in huge evangelic parades to save
sinners (mainly prostitutes and drunks). The Bethlehem
Institute hosted the guest marchers when they marched by. More
than 400 arriving Spiritual Christians witnessed this event.
Years later the Russian prophet Bezayeff also performed
spiritual "maneuvers" (маневров : manevrov). Bezayeff
probably trained marchers in the Stimson-Lafayette
Industrial School lot before taking his spiritual troops to
the streets. At least one of his spiritual marches went to
City Hall, a 1.5 mile (2 km) round trip. Bezayiff could have
been inspired to march from the American Christians in 1905,
or from Community Doukhobors led by P.V. Verigin who also
conducted marches (Маршировку) and "maneuvers," which Sons of
Freedom later interpreted as prophecy for their own glavnoe
pokhod (Great Trek) and song in 1962. (Berikoff, Ahna. "Songs
of Existence: Sons of Freedom Doukhobors Within Time,"
PhD dissertation, School of Child and Youth Care, University
of Victoria, British Columbia, 2013, pages 224-225. )
Despite the fact that the gas works (built in 1912), a soap factory
and a brewery were located on the perimeter of the area, it was
still primarily a residential district, populated mostly by immigrant Jews, Mexicans, Japanese and
others (33 nationalities) with a
good school in the very center of the area. The Amelia Street
School where Berokoff and many
pioneer families attended classes became for many Spiritual Christian Molokan children, from 8 to 14 years old, their first
contact with American culture.
3. Dr. Rev. Dana W. Bartlett, Bethlehem Institutions
Dana
Webster Bartlett was born in Maine in 1860, graduated
college in Iowa 1882, taught in Utah. He continued his
education at a theological seminary in Connecticut 1884 and
graduated from the Chicago Theological Seminary in 1887; and
the same year was ordained a Congregational Minister,
married Mattie McCullogh, and was assigned as a Pastor in
Missouri. In 1892 he returned to Utah. In 1896, at age
36, he was assigned to Los Angeles as Superintendent
of the Bethlehem Institutions (1896
-1914). They had 5 daughters. He published
4 books (1907, 1911, and 2 in 1923). In 1911, he earned a
Doctorate in Divinity. He was appointed to the Los Angeles
City Housing Commission (1909) and Planning
Commission (1910), California
State Commission of Immigration and Housing (1912), Pacific
Coast Immigration Study League (1912), and Pacific
Coast Immigrant Congress (1913). After losing Bethlehem in
1914, he served as Pastoral consultant to First
Congregational Church, Los Angeles. He died in 1942, age 81,
and was Buried
Inglewood Park Cemetery. Many Spiritual Christians
from Russia attended and sang at his funeral.
Within the area there was also a Congregational church and a settlement
house* managed by a sincere devout
Christian, the Rev.
Dr. Dana W. Bartlett who was the first American-born to befriend the Spiritual Christians Molokans in Los
Angeles and who later became a close friend of their leading
elders and who was also very helpful to them in many ways and
was respected by all who came in contact with him.
Learning of this, the parents of the girl, helpless in
their grief and ignorant of the ways of the new country [pluralism?]
enlisted the aid of the leading elders and retained a
Russian speaking attorney (probably Mark Lev, or Constantine M. Mooslin)
to have the marriage annulled.* But of course the sympathies
of the public, the police and the courts** were with the young couple,
especially after the girl informed the court that she fled her
home to evade being sold in marriage to a BSCR Molokan boy she
did not love.
* There was no
legal registered marriage to "annul" (cancel).
** Berokoff injects "police and the courts" with no
context, which I try to provide below.
The parents, in answer to that charge*
in court, explained that it was a
custom among their people to arrange marriage for their children
as in the old country, and as there were more
BSCR Molokan boys of
marriageable age in the BSCR Molokan community
than girls, there was much competition for available girls, and
since their daughter was in such a demand, the parents of one
suitor offered to reimburse the amount of the girl's passage to
America if their son was accepted as a suitor, further explaining
that PAGE 39
the negotiations were still in the preliminary stage and
that there was no intention to force the girl into marriage
against her will.
* Berokoff appears to have
confused his historical timeline. Below I show that while 2
incidents occurred in 1909, the Prygun "bride-selling" scandal
in Los Angeles did not appear as a national sensational news
story for another 3 years, in December 1912.
Although the elders and friends
supported the testimony of the parents, the court was not
convinced and the marriage was allowed to stand.
The newspapers, as usual, made a sensation of the case,
playing it up in headlines for about 6 years a week before
dropping it for other sensations, and after the judge, Curtis
Wilbur, offered to redo all illegal marriages for no
charge.
This is a classic example of "historical negationism",
"historical denialism", "distortion of the historical record",
"deletion
of knowledge", and an "inconvenient truth".
Berokoff accused the newspapers of making a "sensation" and
"playing it up" for a short time "about a week". Newspaper
reports about BSCR kids rebelling against their arranged
marriages began in 1909 and continued in 1912 though 1915,
about 6 years before these young immigrants learned to
register marriages, thanks to the legal counseling of Judge
Wilbur.
Berokoff's oral history postscript of wayward youth is a typical
ethnocentric warning about the dangers lurking in the outside
world. The parents held back their forgiveness for a long time
but eventually relented, but in any case the marriage eventually
broke up and the woman returned to the Prygun
Molokan
community and died soon after and was buried without being
accorded the full Prygun
Molokan
rites.
Berokoff avoided reporting details: names,
ages, case numbers, plaintiffs, defendants, dates, charges, or
congregations. We know Berokoff and others proofread and
edited Young's The
Pilgrims of Russian-town (1932), which also
avoided these facts. Compare Berokoff above to Young's sparser
history, page
108:
"The selection of a partner by
the parents is rooted in familial organization. All members
of the older generation were "given away" by their parents,
and frequently without much previous intimation as to the
prospective mates, who accepted the parents' choice without
much reflection. The Pryguny Molokans
tell of only two cases of suicide because of dissatisfaction
with parents' decision regarding the prospective mate. In
America, however, the children are allowed to choose for
themselves ....
"There are hardly any marriages for money ... social and
economic organizations make such marriages almost an
impossibility."
Berokoff refers to "an event" in 1909
which was in the news for "about a week." Young reported "two
cases of suicide" and arranged marriages are "In America ...
almost an impossibility" . In contrast, the many news reports
up to the 1920s suggest that both Berokoff and Young denied,
negated and/or revised history. The "1909 ... event"
reported by Berokoff cannot yet be correlated with a single
incident reported in the Los Angeles news, which suggests he
is reporting an event not covered in the news, or he scrambled
his oral history timeline again.
Newspapers reported many cases of child abuse
and forced, arranged and unregistered marriages from 1909
through 1915 in Los Angeles county, among all peoples
including Spiritual Christians from Russia, and from 1911
through 1920 in Arizona, among Pryguny and Maksimisty.
For a century, into the 2000s, oral history reports zealous
traditional control of dating, marriage and divorce, with
hundreds, probably over a thousand, banned and bullied from
their heritage Dukh-i-zhiznik faiths. The total
number of cases, types, the defendants identities and outcomes
is vast and affected nearly every family. My parents had fits
of anger who I dated in California, and my mother chased one
girl away from me shouting and running after her to keep away.
Here I summarize cases from a few public records. Names are
spelled as published.
- 1909
- On Sunday 25 April
1909, during the largest annual
communal celebration of their immigration to America,
attended by "More Than 2000" Russians, a failed
murder-suicide shocked the community. Because
sweethearts Alexis Kottoff and Anna Sossoeff (sic) were
forbidden by her father to marry. Alexis Kottoff 23 shot
Anna Sossoeff 16, and shot himself. Both nearly died in
hospital. He was imprisoned 5 years. Zealous father Alex
Sossoeff was in debt and needed his daughter to work for
him, and not marry an educated liberal "freethinking" (Molokan?)
boy from a different faith. Read articles in the Los
Angeles Herald :
- In August 1909, widowed
Willie John Kobzeff, 22 (parents: John and Mary),
married Lillian Clarke 34 (parents English and
Scottish), at the Boyle Heights Methodist Episcopal
Church. In October
1909 news reported his relatives broken up the
marriage, told Lillian he had a wife in Russia, and
shipped Willie back to Russia.
- 1910 — "Stories of White
Slavery Among Russian Immigrants at Honolulu Refuted,"

- In December 1911, a Molokan
girl (Annie E. Shubin) married an "American" with no
public outrage or court hearings. — "Marriages,
Births, Deaths : Marriage Licenses", San Francisco Call, December
13, 1911, page 4, column 5.
- 1912-1915 — For nearly 3 years,
a series of "bride-selling" court cases in Los Angeles by
immigrants from Russia made national news, first focusing
on Elsie John Navikoff who protested her arranged marriage
for $500 (a record amount) and beating by her father.
Fortunately she worked as a maid and her wealthy employer
hired an attorney, maybe Mark Lev, or another Russian Jew.
A "mass meeting" was held at Klubnikin sobraniya
(the "basement"; Russian: podval) meeting hall) on
Clarence street on 24 December 1911 to petition the
Governor of California to investigate and apologize to the
Spiritual Christian immigrants from Russia in Los Angeles.
This petition was probably never mailed to the governor,
as we could not find it in the Hiram
Johnson papers, 1895-1945. 100s attended the court
hearings, about which news was published across the
country describing how their sacred traditions from
Russia were not legal in the United States, their land
of refuge.
The initial bride-selling investigation was conducted by
the foremost federal expert of the time, Captain Charles
T. Connell, chief
of the Southern California Immigration service (1911-1931).
Connel was the U. S. government specialist in
"white-slave traffic". ("Arizonan Conducts This
Investigation : C.T. Connell Begins Examination
into Alleged Sales of Girls by Parents", Bisbee
Daily Review, January 10, 1912, page 1)
Fortunately the legal hearings were under the
jurisdiction of Judge
Curtis D. Wilbur, a member and youth leader at the
First Congregational Church, a board member of his
church which sponsored Bethlehem Institutions who worked
with Dr. Rev. Bartlett. Judge Curtis Wilbur knew the Dr.
Rev. Bartlett and many of the
Spiritual Christian families from Russia due to previous
cases in his Juvenile Court. The judge imposed no
punishment, but ordered the Spiritual Christians
from Russia to obey U.S. laws by promising they would no
longer exchange money for brides or arrange marriages,
to legally register marriages, and to not physically
punish their kids. Judge Wilbur offered to re-do all
unregistered marriages legally in his court for no
charge (pro
bono). The first to be married by this noviye
obryad (new ritual) was a son of leader F. M.
Shubin who set the example for others in the city to
follow. Those who had fled the city were able to
maintain an isolated culture for a few more years, like
colonies in Arizona and Utah (below).
There are different terms for the same process of families
joining in agreement before their kids marry. Today,
western Dukh-i-zhizniki say chay zapivat’ (чай запивать : to
drink tea), shortened to chay (tea). In Russia the same Dukh-i-zhiznik gathering
is called a svatovstvo (сватовство :
matchmaking). In Canada Dukhobortsy
say zapoy.
(запой : drink a lot [of tea]).
- 1912 — Simultaneously and
very similar to non-Doukhobor Spiritual Christians in
Los Angeles, in British Columbia (B.C.), Canada, the
Christian Communities of Universal Brotherhood (C.C.U.B.),
communal
Doukhobors (obshchei dukhobortsy),
were accused in court of 4 allegations, which were legally examined in public hearings
for 4 months, in 3 towns in B.C. and 4 towns in
Saskatchewan (S.K.). Testimony was gathered from 110 witnesses aided by several lawyers and
scholars. The 3rd allegation was substantiated but not
prosecuted: "(3.) It was objected that the peculiar
[home] marriage ceremony, the fact that the Community
recognizes no outside authority, and that it refuses
to register births, deaths, and marriages,
... " Obshchei dukhobortsy also
objected to the Public Schools Act. For
violations, the
commissioner recommended fines to be more
effective than jail. (William Blakemore, Report
of Royal Commission on Matters Relating to the Sect
of Doukhobors in the Province of British Columbia,
1912, page 64.)
- In December 1912, Robert
S. Sparks became the deputy in charge of the
marriage-license division of the office of the County
Clerk of Los Angeles, where he served until 1920. He
reported that during his 8-year tenure, he issued more
than 200,000 marriage licenses (25,000/year). He was
nicknamed "Cupid" because he got thousands of letters
from single men and women for matchmaking help which
he answered with the help of his wife, resulting in
hundreds of marriages. In 1921 he was elected to the
Los Angeles City Council for a 2-year term. Sparks'
office issued marriage
licenses for the Spiritual Christians from
Russia.
- 1914 — In the same year that the
Bethlehem Institutions closed, 2 tribes of
Spiritual Christians organized their escape
from the city. Their Russian-speaking
attorney, Constantine M. Mooshin, cited these
4 reasons in court::
- The tango and other late
[modern] dances.
- Styles of women’s dress,
including the slit skirt [an improvement of
the hobble
skirt, also "peek-a-boo" and "open"
dresses and shoes were controversial.]
- The wearing of pretty hats
instead of shawls [by women].
- The American marriage laws
which do not recognize [unregistered]
Russian marriages.
- 1916 — A new Hollywood silent
film "Sold
for Marriage" is promoted about a young Russian
village girl sold for marriage in America. This nationally
shown film may have enhanced and prolonged the impact of
the public perception of bride-selling among all Russians.
It appears to be inspired by the Novikoff case in Los
Angeles.
- 1920 — 2 Arizona presbyters
(persvitery) were together fined $600 (= $9,200 to $22,000 in 2021)
for not registering marriages since 1911. Many who
believed they were being persecuted for their religion in
Los Angeles fled to other states. Maksimist Mike
P. Pivovaroff, who founded the first of four colonies in
Arizona in 1911, was jailed. Prygun presbyter
Homer (Foma) S. Bogdanoff avoided arrest but also appeared
in court. Their lawyer entered pleas of guilty. They were
fined $300 each (about year's laborer wages each, or the
cost of a house or car at the time) and ordered to re-do
all marriages legally. Their lawyer also testified that
the defendants recently learned that burial certificates
were required, but no charges were filed for those civil
crimes.
To not offend the most zealous elders,
the American-born youth of Spiritual Christians from Russia
learned to first get their civil marriage license at the
courthouse, before they did their "church wedding." For
expedience many drove to Las Vegas, Nevada, or Yuma, Arizona,
to get married and return, perhaps because no blood test or
birth certificate was needed then. (If anyone knows, please
reply —
administrator (at) molokane.org.) By the 1950s a few bolder
presbyters learned they could sign the marriage document and
gladly did at the end of the full wedding day; but the more
zealous presbyters
refused to sign any government (Caesar's) paper, which
forced engaged couples to comply with different laws "inside"
and "outside" of their congregation.
Definitions — What
are we talking about?
During the Los Angeles court hearings,
non-Spiritual Christian witnesses who spoke Russian
(Orthodox, Jewish) testified that what the journalists
called "bride selling" has been a tradition in
Euro-Asian countries for centuries where a child's
destiny is assigned by parents —
matchmaking.
In the early 1900s the practice of buying a wife was
strange and/or unfamiliar for Americans in government
positions who were White
Anglo-Saxon Protestants (WASPs, Northern
European immigrants), many who knew of their
traditional Protestant dowry,
and maybe wreath
money. The "bride selling" custom from Russia
(Eastern Europe) seemed illegal to those whose
ancestors gave gifts to newly weds after a
wedding (as a gift), but not to the family before
a wedding (like a bribe or a fee).
In contrast to Northern European customs, the Eastern European
Spiritual Christian immigrants from Russia were
practicing an Old World custom variously translated
today as bride-price, bride-wealth,
bride ransom,
wedding ransom,
and bride buying (payment for the bride to her
family). The common terms in Russian are kalym (калым),
kladka (кладка),
vykup nevesty (выкуп
невесты) and svadebnyi vykup
(свадебный
выкуп). A common Russian term for a girl
getting married is "to leave [the family home] for
the husband" (выйти замуж : vyiti zamuzh),
to probably live and work in her husband's extended family rural village.
Though these terms do not appear in the Russian
Synodal Bible used by the accused,
defendants, they were familiar with the customs
and labels.
In the Russian Old Testament (RUSV),
the Hebrew Bible emphasized by Subbotniki,
Pryguny, Maksimisty, Klubnikinisty,
etc., a different term appears once in Genesis and
twice in Exodus — veno (вено).
The term veno becomes
clear in modern Russian
Bibles (SZ, NRT), and in some English
translations.
| Russian Synodal Version
(RUSV) |
Slovo Zhizny (SZ,
NRT)
|
English Standard
Version (ESV)
|
Бытие
34
(12) назначьте самое большое вено
и дары; я дам, что ни скажете
мне, только отдайте мне девицу в жену.
|
Бытие
34
Назначьте за невесту любой выкуп и
подарки, и я заплачу, только отдайте мне ее в
жены.
|
Genesis
34
(12) Ask me for as great a bride-price
[engagement present] and gift as you will, and
I will give whatever you say to me. Only give
me the young woman to be my wife.
|
Исход
22
(16) Если обольстит кто девицу необрученную и
переспит с нею, пусть даст ей вено
[и возьмет ее] себе в жену;
(17) а если отец не согласится выдать ее за
него, пусть заплатит [столько] серебра,
сколько [полагается] на вено девицам. |
Исход
22
(16) Если человек соблазнит девушку,
которая не давала обещания выйти замуж, и
переспит с ней, он должен заплатить свадебный
выкуп, и она станет его женой.
(17) Если отец откажется отдать ее ему, он все
равно должен заплатить выкуп, какой
полагается за девушку. |
Exodus
22
(16) If a man seduces a virgin who is not
betrothed and lies with her, he shall give the
bride-price for her and make her his
wife.
(17) If her father utterly refuses to give her
to him, he shall pay money equal to the
[higher] bride-price for virgins.
|
A
misunderstanding can easily occur if the reader
only consults the King James Version which uses
the Northern European terms "dowry" and "endow her," which has a different
meaning. Compare many English
parallel renderings of Exodus 22:16 to see that 12 Bible translations
chose the English term "dowry" and 13 chose "bride
price", about even.
In 2011, I was invited to witness and document a kalym
performed east of Seattle, Washington, during a
wedding of young Adventists from Russia, who are descendants of Molokane.
About 200 immigrated in early the 2000s, most from
Krasnodar
province, Northern Caucasus, Russia. Years later,
via DNA analysis, I learned I was distant cousins
with the groom's family. For interested
readers, a sample of kalym
appears on a video of
a Doukhobor wedding recorded in south Georgia
S.S.R., in 1987, and can be seen on the Internet.
Both of these groups from Russia may have modified
their traditions during Soviet times. In the
Doukhobor community in Georgia S.S.R., the groom
had to pay ransom (vykup
: выкуп) for his
bride's stolen/missing shoe. In Washington state
in 2011, the Adventist groom from Russia gave a
gift credit card to enter the bride's house. In
both cases the boys had a lot of fun negotiating
with loud laughing persistent bridesmaids who
ganged up to block the entry door, acting as
agents for their bride and demanding the highest
price possible. See the first 11 minutes of The
Doukhobors, Episode 7. (The entire
documentary film is nearly 4 hours, with
approximate English subtitles.)
For many faiths rooted in Old Russia, kalym is part of
their traditional wedding ceremony. Unfortunately,
the custom of the "brides house" (devichnik :
девичник),
uzel (bundle of tableware gifts), and
other folk customs and foods have faded from use
among the diaspora Spiritual Christians, often
replaced with "American" forms, which are less
embarrassing, less effort, and/or easier to buy
than make.
The most zealous Spiritual Christians that
immigrated to Southern California apparently
practiced a variation of kalym
in which the parents
negotiated and collected the bride price in
advance, then told their kids who to marry. Some
promised, or betrothed, their kids as young as
babies by "notching the cradle," common among
Spiritual Christians isolated up to the mid-1900s
in Mexico and Iran (Persia).
|
Though the court
cases in Southern California (1911-1915) and Arizona
(1920) may have stopped illegal "bride-selling," it did
not deter zealous parents from
imposing other controls on children who were rewarded with
wealth (houses, land, rubbish trucks, money, inheritance,
etc.) for marrying "right", or disinherited and/or banished
for marrying "wrong." Many young marrieds have been lavished
with gifts for obeying family, and many have been ostracized
for not obeying.
In 1984, Susan Leo Tolmachoff killed herself in Arizona with a
hand-gun after her irate delusional father and his relatives
forbade her to marry a divorced fellow in Kerman, California — Bill Pete ("Bosco") Nazaroff. Within a few
years, her mother Jean M. Dobrinin-Tolmachoff, divorced her
abusive husband. Many tragic cases exist of dominant parental
control regarding marriage. I know of banishment, no
inheritance, cases that occurred in the 2000s.
In contrast to continual zealous parental control to marry
into an acceptable, spiritually clean, Dukh-i-zhiznik family,
the assimilated families often advise, and some demand, that
their children marry out of the Spiritual Christian faiths so
they can invite their American (or Australian) friends to an
American (or
Australian) church wedding and reception, and will
not have to perform a long traditional costumed Spiritual
Christian ceremony in Russian, kiss the same sex and old
people, and be obligated to attend in-law (svakh :
свах) family services for the rest of their life.
Though "bridewealth" was proposed in 1931
as ms to me to be a more accurate term, "bride-price" appears
in recent news online:
- In
China, Marriage Rates Are Down and ‘Bride Prices’ Are Up
: China’s one-child policy has led to too few women.
Grooms are now paying more money for wives, in a tradition
that has faced growing resistance. by Nicole Hong and Zixu
Wang, New York Times, March 26, 2023 (Print
version, page A4, "In China, a Surplus of Single Men Means
‘Bride Prices’ Are Up.")
- Bride
Price: 'My husband can't afford me', by Nyasha
Michelle and Celestina Olulode, BBC, 27 January 2020.
- Chapter 6: "Bride
Price and the Well-Being of Women," by Sara Lowes,
Nathan Nunn, in Siwan Anderson (ed.) et al., Towards
Gender Equity in Development, Oxford Academic, October 2018, pages 117–138.
- An
Ex-Husband Can No Longer Demand A Refund Of The 'Bride
Price', by Amy Fallon, National Public Radio,
NPR, August 21, 2015.
- For
Chinese Women, Marriage Depends On Right 'Bride Price',
by Louisa Lim, Morning Edition, National Public Radio,
April 23, 2013.
- Heated
debate as MPs ban bride price refund, by Mercy
Nalugo, Daily Monitor, March 4, 2013.
- Do
marriage contracts and payments affect divorce?
(my title), Dan Phung, paper for Anthropology 174 (Dr.
White), University of California at Irvine, 2002-2007.
- The
Economics of Dowry and Brideprice, by Siwan
Anderson, Journal of Economic Perspectives, v21, n4,
Fall 2007, pp. 151-174.
- "Bridewealth"
vs. "Brideprice", by George Dalton, American
Anthropologist: New Series, v68,n3, June 1966,
pages 732-738.
The last article above by Dr.
Dalton explains that, in English, "bridewealth" is a better
fitted scientific term than "brideprice". He argued: "To use
the term "brideprice" is to im
ply that payment at marriage is a market or commercial
transaction and therefore that marriage entails a commercial
purchase of rights or services."
A rough search of online databases found these results on November 23, 2023.
Database
|
Brideprice
|
% |
Bridewealth
|
%
|
Google
|
4,620,000
|
92.6%
|
368,000
|
7.4%
|
Bing/Yahoo
|
9,030,000 |
99.7%
|
30,600 |
0.3%
|
| ESBSCO |
1,386 |
23.8%
|
4,439
|
76.2%
|
JSTOR
|
2,102
|
22.4% |
7,260
|
77.5%
|
Many such incidents This unfortunate incident caused some Spiritual Christians from Russia the Molokans to
have grave misgivings about their decision to live in the city.
But even before these this
incidents the leaders and some of the people in general realized
that a permanent settlement in a city should not be considered.
It was bearable as a stop-gap, a place to recuperate, to
replenish the pocket book, but under no circumstances as a place
of permanent settlement for simple, religious peasants.
Why did most stay in the metropolis, divided
into separate tribes? Berokoff does not explain why most
stayed in their kingdoms in the city, including himself.
See: Conclusion, last page 155.
Though
many Spiritual Christians from
Russia, led by the most zealous, fled from Los
Angeles to rural colonies, and a few back to Russia,
claiming they were being persecuted by American laws
allowing girls marry whom they want, mandatory marriage registration, foreign dress
and education. Those in San Francisco and northern California,
had fewer legal problems mainly because the all the zealous
tribal faiths were clustered in Southern California. In San
Francisco the Spiritual Christian Molokane met
Spiritual Christian Baptists from Russia immediately attended
school, marriages were registered, many parents allowed
interfaith marriages. However, problems with youth delinquency
and elder resistance to naturalization was about the same in
Los Angeles and San Francisco due to the clash of their
foreign rural peasant culture with metropolitan life, and high
density population with other immigrants, nationalities and
faiths.
In Canada, arranged marriages with a "customary payment [by
the groom] for the bride" was a tradition among Mordovian
Doukhobors, who retained this tradition after joining the
"spirit-wrestlers." In Central Russia, Spiritual Christians,
including ancestors of Doukhobors, lived among Mordvins,
promoted intermarriages, learned Mordovian languages and
songs. A Moksha-Mordovian-language
wedding song was also preserved in Canada.* Mordvins joined
Doukhobors in 1802, when Doukhobors were permitted (by order,
ukaz) to settle in Tavria (Milky
River area, New
Russia); and they were also granted religious freedom,
5-year tax exemptions, 10-year interest free loans, free
transportation, and 40 acres of land to each settler along the
west bank of the Molochna River.** Many Mordovians evidently
liked the deal and joined the migration as new Doukhobors. In
1805, 3 years later, Molokane were similarly given
religious freedom and permitted to migrate to the east side of
the river, south of the extensive German
Mennonite Molochna Colony. More Mordovians may have
arrived to join the legal Molokan migration. In Novorossiya
(New
Russia), during the 1832-1834 famine and "great
outpouring of the holy Spirit" recorded in Dukh-i-zhiznik
oral histories, the origins of what would become Pryguny/
Sopuny/ Skakuny /Shalatupy occurred
among the these mixed populations, probably because piest Harmony
Societies from Germany (Harmonies) traveling from
Württemberg
(home of Martin
Luther and territory of the Protestant
Reformation), to Palestine (or Mount
Ararat) beginning in 1817, enticed those who were most
susceptible to zealous religious ecstasy and awakenings, and
apocalyptic prophecies to witness the second coming of Christ
in 1836.*** Some of the ethnic Mordovians joined the zealots,
and migrated with them in the 1840s to the Southern Caucasus,
where a clan settled in Shorzha
village, on the mid-east bank of Lake Sevan, now in
Armenia.
* Sushkova, Yulia N. "Anthropology
of migration: the experiences of the Doukhobors in Canada",
Journal of the Geographical Institute “Jovan Cvijić”,
65(3), pages 436-437.
** Kalmakoff, Jonathan J. Resettlement to Molochnaya, page 5
of: "An
Overview of Doukhobor Settlement and Migration",
Doukhobor Genealogy Website, June 24, 2012.
*** Gestrich (Trier), Andreas. Chitiastic Pietists, "German
Religious Emigration to Russia in the Eighteenth
and Early Nineteenth Centures: Three Case Studies", in
Lehmann, Hartmut and Hermann Wellenreuther, editors, In
Search of Peace and Prosperity: New German Settlements in
Eighteenth-Century Europe and America, Penn State
University Press, 2010, pages 92-98.)
In Russia they Spiritual Christians were
accustomed to independent life of a villager who tilled his
land, planted his buckwheat, rye and
wheat, raised enough potatoes, cabbages, carrots,
dill, sun flowers, cucumbers and other vegetables for
his own use. There he could take time off for his annual
holidays and when winter snow
came, he rested for five or more months until the next spring
whereas here, he, as well as his wife and the older children
were in a set routine of nine and ten hours at work under the
stern and watchful eye of the foreman six days a week, month
after month and year after year, begging the foreman for time
off for the annual holidays and, more often than not, losing his
job for the devotion to his faith. But worst of all, there was
no prospect of improvement in the routine.
PAGE 40 Some families,
especially those who were comparatively well off in Russia, were
soon disillusioned with America and returned to their village
homes in Russia but, with exception of these few and despite the
hardships, the great majority of those
already in the U.S. heeded the advice of Klubnikin [Klubnikinisty],* and being encouraged by elders who
were steadfast (postoyannie)**
in the belief of Klubnikin's prophesy, refused to consider the
idea of return but began to look around for other means to
escape the drudgery of city life, particularly to found a
farming community somewhere, a desire that henceforth was never
out of their minds.
* Berokoff falsely states
"the great majority heeded the advice of Klubnikin" probably
to promote his branch of his Dukh-i-zhiznik faith.
He does not attempt to acknowledge the broad spectrum of many reasons
Spiritual Christians did not return to Russia, nor
that the majority were not Klubnikinisty like him.
** "Steadfast" is translated here into Russian to show the
reader how the word is used positively by Dukh-i-zhizniki
in context when describing their faith movement, but
negatively about Molokane. When describing Molokane,
postoyannie is an insult; but when describing Klubnikinisty,
postoyannie (steadfast) is a virtue.
The above paragraph suggests that
Klubnikin did not believe Rudomyotkin would return nor that
all must soon return to Russia to meet him and Christ on Mt.
Ararat. This indicates that Maksimisty have different
beliefs than Klubnikinisty who remained in their
foreign metropolis abundant with free social services, low
cost transportation, food and housing with plumbing and
electricity.
6. Mexico
Colonies
"During the long reign of [Mexico President] Porfirio Diaz ...
(1877-1910), the Mexican government encouraged the
establishment of communal settlements for natives and
immigrants. Some 60 colonies were started, 44 by
private initiative and 16 by the government. Settlements from
the United States formed 21 communities, the 10 listed* and
the 11 by Mormon schismatics." (Pitzer, Donald E., ed. America's
Communal Utopias, University of North Carolina
Press, 1997, page 475)
* Pitzer's list does not
show the Guadalupe colony, perhaps because it was not a true
commune, perhaps missed, though on the following page 476 is
listed "Molokan Community (1911-?); Glendale, Arizona,"
which was 3 miles west of Glendale. Anyway, note that about
"60 colonies were started" of which Pryguny were at
least one.
Before such a colony was established in the United States,
agents for a large tract of land in Lower California, Mexico,
learning of the immigrants' Molokan
desire to establish a farming community, contacted them early in
1905 1906 with a proposition to sell them the
tract which was called Ex-mision
Rancho Guadalupe and on terms within reach of people who were
still impoverished from their emigration from Russia.
Plans for Spiritual Christian colonies in
Mexico were first considered about 1900 due to inquiries by
mail and scouts. A personal history, with many errors and
omissions, appears in Mohoff, George. The
Russian Colony of Guadalupe: Molokans in Mexico,
self-published, 1995. Mohoff's book will be corrected later.
Mainly Pryguny
colonized Mexico. More
information with maps. Below I refer to Mohoff's book as
"Mohoff."
This tract of land consisting of 13,000 acres [20.3 square miles] was located 60
miles south of the United States-Mexico border, in a pretty
valley through which flowed a small stream but which turned into
a torrent after a rain storm. The dry-farmed
land was capable of producing a good crop of wheat in a rainy
year but was also subjected to cycles of dry years in the same
manner as other sections of California.
In any case, 50 families were attracted to the proposition to
purchase the tract. Led by Vasili Gavrilitch Pivovaroff and Ivan
G. Samarin the land was bought for the sum of $48,000 $40,000 (Mohoff,
page 12) and a site was selected for a village in
the style of their native Russia, except that, for lack of logs,
the houses of Russian design and plot
layout were built of adobe in the style of Mexico. Adobe, mud-bricks, are also common in Russia.
I.G. Samarin and C.P. de Blumenthal signed the contract as
agents for the "Russian colony."
Mohoff (page
15) reports: "The land was leased in November 1905 and
ultimately purchased from Donald Barker on Feb. 27, 1907." I
believe (with no direct proof yet) that Los Angeles attorney and
investor Donald Barker acted as a broker, not a "seller,"
and offered a deal that the immigrants could not refuse. He
got them onto land with supplies for no, or little, up front
cost, and they would pay him back with wheat, not cash. The
land was owned by the Mexico government and sold as "public
land" at $2/acre to foreign investors.
The price for Baja public
land sold to foreign colonists was set by the Mexican
government at $2/acre, but these colonists from Russia paid
85% more — $48,000/ 13,000 acres = $3.69/acre. Why? Because
they asked for supplies
(wagons, animals, building materials, food, etc), the bank has
loan fees, and Barker probably added his fee/commission, which added $22,000 to the land price.
Because
Barker worked with several banks in Los Angeles and had
investments in Mexico, he probably created a business entity
which he owned, or was a primary owner and represented, and
arranged the loan for the purchase through a bank in Los
Angeles. The "down payment of $5,700" (Mohoff,
page 12) could have been (a) earnest money he
collected in cash, or (b) a paper amount wrapped into the
loan used for bank fees and/or commissions. I favor (b)
because $57,000/ 104 families = $54.80/ family for the down
payment, which, at a dollar a day wages in Los Angeles, was
nearly impossible to pay, and the goal was to get these
immigrants out of Los Angeles as soon as possible before the
next immigrant wave came in, as reported in the press.
To collect the loan payments, Barker arranged for the new
Pacifico flour mill to be built in Ensenada where each
immigrant farmer, land purchaser, paid for his share as
shown in Mohoff,
pages 14-15. Why a flour mill? Probably because a
similar colony in the San
Quintín valley, about 120 miles south of Ensenada had
a flour mill ....
[ADD MORE]
Barker's
law partner was Senator
Finch. Barker appears on many
new corporation board of directors, including a Los Angeles
bank and and a land investment company in Mexico.
Mohoff is wrong
page 9, page 15 — land bought from Donald Barker Feb 20, 1907
More likely Barker's bank loaned money and he brokered the
sale of land owned by Mexican government to colonists, as done
for many other settlements.
Soon a colony was established which was to exist until well into
the middle of the century, becoming in time a tourist attraction
because of its quaint, old country appearance and atmosphere.
PAGE 41 But in founding
the new community, they adhered strictly to the age-old method
inherited from their forefathers. Thus, instead of each family
building a homestead on his own farm for more efficient
operation as is the custom in America and other countries, a
central site was chosen for the entire community where a village
was established.
Each individual was therefore compelled by necessity to
transport his implements to his farm periodically to plow and
cultivate it and harvest his crops in the summer, camping there
for days at a time, coming home on weekends for a visit with his
family.
A writer who visited the colony in 1928 had this to say of their
farming methods: "The founding of a large village in Guadalupe
Valley is indeed contrary to any practical consideration and is
to be explained only by the existence of an old inherited
juristic notion, too deeply rooted in the minds of those
peasants to yield before any environmental influence. Distance
from the fields were largely such that men were unable to return
to their homes in the evenings but often camped on their lots
for weeks. Inconvenient conditions such as are typical for
Southern Russia are thus repeated where they could be easily
avoided. [Footnote: Oscar
[Oskar] Schmieder* in "The
Russian Colony of Guadalupe Valley" as quoted from the "Pilgrims
of Russian-town," page 253.]
* German geographer and expert
in the regional geography of Latin America.... University of
California at Berkeley, ... Associate Professor from 1926 to
1930. Wrote: "The Russian colony of Guadalupe Valley,"
Berkeley, Calif., University of California Press, 1928.
It is true that the method was inconvenient and inefficient, but
the writer failed to perceive that it satisfied the colonist's
hunger for companionship and spiritual sustenance in a strange
land amid surroundings inimical to preservation of the
brotherhood. It is to be noted that in 1911, when a Maksimist
Molokan colony was founded near
Glendale, Arizona, the same method was followed.
There were other examples of extreme allegiance to the methods
of the forefathers which are rather astounding from the American perspective: PAGE 42
- The title to the whole tract of land was vested in the
names of three trustees.
- No grant deeds or other evidence of ownership were issued
to the individual owners. The names of individual owners
were simply recorded in a community book, which was
entrusted to a person elected for that purpose.
- A government surveyor never officially surveyed the land
nor was the subdivision recorded in government archives.
Apparently, to save the cost of a qualified surveyor, they
chose the method that was used by their fathers and
forefathers in Russia. Measuring off a length of rope and
using natural and artificial markers, such as large embedded
rocks or trees, they did the job in their own crude manner
and proceeded to allot the land to the individual owners.
The allotment of individual parcels was likewise conducted in a
very ingenious and typical Russian peasant Molokan manner.
To begin with the whole colony of 50 families were divided into
10 family units of five families to a unit. The whole tract of
land was then divided into several sections, each section
suitable for a certain crop. Thus there was a section of river
bottom land; another section at higher level and suitable for
raising grain, a hill-side section for raising hay and a section
of untillable mountainous land which was left undivided for
community use as cattle pasture.
Each section of tillable land was then subdivided into ten
parcels for which the ten family units proceeded to draw lots
for their share of each category. The family units then drew
lots for ownership of their individual parcels according to the
need of each family. Some were
dissatisfied with the quality of the land they randomly got
and left.
This method was ingenious but crude, yet the amazing fact
remains that, although forms changed ownership through sale
and/or inheritance, the markers remained inviolate and despite
the absence of deeds and of embedded surveyor's markers, never
in the history of the colony were there any litigation to decide
tide to a property notwithstanding the fact that there were PAGE 43 abundant seed for
sowing not only law suits but bloodshed as well. One must marvel
at the innate honesty of those illiterate peasants that knew
God.
However, the passing of a half a century showed that this method
was not only naive but careless as well as dangerous, causing
much anguish and worry to the heirs of the original colonists,
for their sons and grandsons eventually had to struggle to prove
ownership of the land when in 1952 squatters from the city of
Mexicali, discovering that no deeds were recorded to some of the
colonist's land, forcibly settled upon the land and despite the
intervention of Federal, troops, at times successfully claimed
ownership thereto through squatters rights.
This proved to be the straw that broke the back of the first and
most successful Spiritual Christian
Molokan
attempt at farm colonization in America. After these raids of
squatters (Spanish: paracadistas) all but a very few
families emigrated to the United States, and the colony as such
ceased to exist.
Economics was much
more significant than squatters. These Russian colonists
either sold their land cheap or voluntarily abandoned land
they legally owned to move to California. Ironically, many
of these Spiritual Christians left Russia to avoid war taxes
and a revolutionary recession, and moved to Mexico to
another civil war with taxes. While these Russians got
settled in Mexico, those remaining in Russia got religious
freedom and less taxes, which lessened their desire to flee
from Russia. The Mexican Revolution began in 1910, and war
taxes were levied which raised costs for importing farm
equipment and exporting wheat.
In January 1916, a
group of 120 people, most from
Tyukma village, Kars oblast, were the first to leave Mexico as a group. They
were directed, perhaps by tycoons in Southern California, to
farm 3000 acres near Jerome Junction, Chino Valley, Yavapai
County, Arizona. In Mexico they were the Tyukma
congregation, but in America they were called Dzheromskyi.
(Jeromskyi) Within 8 months they did not get
irrigation water as promised and abandoned Yavapai County. All sued the land
company. Some went back to Mexico, a few
to Los Angeles. The majority resettled at the north
end of 3 other Spiritual Christian colonies, 2 miles west of the town of Glendale,
Arizona, 13 miles north-west of Phoenix. Within
5 years most left Arizona in the 1920s to California.
In
1938, a smaller group began moving from Mexico to Ramona,
north San Diego county. The bigger exodus to the U.S. began
after WWII when the Prygun youth in Mexico realized
that wages were much higher in the U.S. George Mohoff
explained that a friend, who moved to Los Angeles a year
earlier, drove back to to visit Guadalupe in his own car.
When he told his buddies that the car was his, no one
believed him. In the 1990s, Mohoff exclaimed something like:
"None of us could ever earn that much money in our lifetime
working in Mexico! That's why I think most really left for
L.A. It was not because of the squatters, it was for the
dollar!"
7. Hawaii Colony
Another most interesting episode in the Spiritual
Christian Molokan
quest for land occurred 10 days after
at about the same time as the purchase of the
Rancho Guadalupe. It seems that an agent for a sugar plantation
on the Hawaiian Islands appeared among them with proposition to
sell them land on the island of Kauai Kuwai, northwest
of Honolulu. Probably J.
B. Castle who had an office in Los Angeles.
Captain
P. A. Demens with his daughter took an exploratory fact
finding trip in September 1905 to Hawaii. He examined 3
islands, one with a Russian settlement. The press announced he
was there "To Encourage Russian Small Farmers ... on a mission
from President Roosevelt..." to potentially resettle up to
20,000 "Molokani or Doucaubori" from the United States and
Canada. He returned to Los Angeles with a positive report.
The proposition was sufficiently attractive for the people to
send a second delegation to
explore the possibility of establishing a colony. Upon their
return, however, the delegation, composed of Captain P.A. Demens, Philip M. Shubin
and Mihail Step. Slivkoff, was in complete disagreement, Shubin
strongly opposed the proposition while Slivkoff urged a
favorable response.
After signing the contract in Hawaii,
Shubin stayed state-side to survey land in Texas, which he
rejected. For about the next 5 years Shubin and others
extensively toured the U.S. and Mexico, probably at the
expense of the railroad land agents, looking for a better deal
than the slums of Los Angeles. most returning to their
"kingdom in the city."
Demens was an excellent salesman. In November 1905, he
submitted a long (3 column, half page) article to Hawaiian newspapers sugar-coating them as the
“cream of Russia’s population — a desirable class of White residents.” (See:
Demens Introduces “Molokans” to
Hawaii)
The upshot of it all was that 20 families and ten men whose
families were still in Russia, 110 people,
including about 34 Molokane, agreed to the
terms and sailed for these islands with high hopes. John Kurbatoff, an educated, well-dressed
Molokan from Harbin, China (known by Pete W. Loskutoff,
San Francisco), was to manage the Molokan Settlement
Association. At this point in the episode there are
different versions from different people. Some insist PAGE 44 that the would-be
colonists were deceived into thinking that they were signing a
contract to purchase land when, in fact they were signing a
contract to work for the plantation for a number of years.
The following account is paraphrased from an article written in
1955 by Yacov Fetisoff and published in San Francisco in the
same year by the Molokan Postoyannaye
Community. [Footnote: The account of 50th Anniversary of The Molokan
Postoyannaye
Life In America, page 167.*] Being
one of the would-be colonists, he relates that, among other
terms, the company agreed to provide the fare from Russia to the
Islands for the families of those ten whose families were still
in Russia and to bring them to the Islands not later than June
1, 1906. In addition to the ten families, the company agreed to
bring in 100 other families from Russia by that date and at no
cost to the immigrants. The names and addresses of these
potential immigrants were given to the company and the
prospective colonists were notified by their friends on the
island to be prepared to join them by June 1, 1906.
* Citation: "Когда и
как поселились в Сан-Франсиско, Калиф., духовные
христиане-молокане," Отчет духовных христиан молокан
(постоянных) по поводу 150-ти летнего юбилея
самостоятельного их религиозного существования со дня
опубликования Высочайшего указа Государя Российского
престола Александра Павловича от 22-го июля 1805 года и
50-летнего юбилея со дня переселения наших духовных
христиан молокан постоянных из России в Соед. Штаты
Америки, состоявшегося 22-23 и 24-го июля 1955 года в
городе Сан-Франциско, Калифорния. c. 167.
("When and how Spiritual Christian Molokans settled in San
Francisco," Report of Spiritual Christian Molokans
(constants) over the 150th year anniversary of their
independent religious existence from the date of
publication of the decree of the Supreme Sovereign of the
Russian tsar Alexander Pavlovich from 22th July 1805 and
the 50th Anniversary of the relocation of our Spiritual
Christian Molokans constants from Russia in the United
States, held on 22-24 July, 1955 in San Francisco,
California. Page 167)
But the company stalled and by various means delayed sending the
passage tickets to those families until the agreed date. They
then notified the would-be colonists that they failed to live up
to the agreement, and that the agreement to bring the other 100
families is null and void but they could remain there as
laborers if they wanted to.
The colonists would not agree to this and gradually, as
finances permitted, they sailed back to the mainland
in small groups at no cost, the
last group arriving in San Francisco late in August October of 1906 when that city was still
in ruins from the terrible earthquake of April 26, 1906.
Thus, to their sorrow and expense,
the Molokans experienced
for the first time the sharp practices of American land sharks.
News reports state that the Spiritual
Christians were treated fair and honest by the government
and plantation owners of Hawaii. Had they stayed in Hawaii
and waited a year for their homesteads, they would have
lived in rural isolation and today the ocean-view land of
each family would be worth many millions of dollars. During
their short stay, 3 leaders opposed each other, their
congregants became impatient, and many preferred the easier
life they had in the slums of Los Angeles.
The following forgotten oral history is
summarized from 100s of news and other documents.
Unfortunately, the Garden Isle newspaper, Kauai, for
this time was destroyed in a tsunami in April
1946, and only a few of their first-hand reports were
republished on other islands.
When sugar prices
increased more than five-fold (500%) during the American Civil
War, Hawaiian plantation tycoons searched the world for cheap
labor to profit from the lucrative
demand. Before 1900, one tycoon went to Russia to
personally petition Tolstoy to send all the Dukhobortsy
to Hawaii, but their arrangements for Canada had been
finalized by the Friends Service Committee, London. Though Dr.
T. Kryshtofovich, a Russian agricultural professor and
neighbor to Demens, had already advised Tolstoy that Hawaii
would be too tropical for Russian peasants, the tycoons in
Hawaii with offices in California, knew that more peasants in
Russia may come to California.
Before I. G. Samarin and de Blumenthal signed a land contract
in Mexico on September 2, 1905, Spiritual Christians in Los
Angeles were already solicited to move to Hawaii along with
all wanting to come from the Southern Caucasus. This would
solve two problems: (1) remove a huge burden from Los Angeles
city services, (2) redirect all incoming Spiritual Christian
to Hawaii (not Los Angeles), and (2) provide much needed
homesteads and cheap white labor in Hawaii.
On September 12, 1905, Captain
P.A. Demens left for Hawaii to scout for these Spiritual
Christians anxious to get their own farm colony. Demens'
report in Los Angeles resulted in a list of 124 (65 families)
households (496 people)
willing to colonize in Hawaii, more than those planing to live
in Mexico.
In November 1905, Demens returned to Hawaii with F. M. Shubin
and M. Slivkoff for a week of negotiating with the governor
for clusters of homestead farms. The two Prygun
representatives wanted land for 5000 settlers, most to
come directly from the Southern Caucasus. They returned to Los
Angeles and after weeks of discussions, signed a contract in
January 1906. Within a month, 110 Spiritual Christians
boarded a boat, less than a fourth who signed up, for a free
ride to their new home. No reason is know why the majority who
signed up, did not go at the last minute, because an entire
ship was about to be rented for all who signed up. 1,500 were
at the dock to see them leave. If they did not like it, they
could come back at no cost. The Molokan congregation
was led by John Kurbatoff, who had a camera and 2 photos of
his group showing of about 34 members have been found. The Prygun
groups were led by Mike Slivkoff, who was often opposed by
at least one other man, of which no group photo has been
found. F.M. Shubin stayed in Los Angeles.
During the trip, a child died (no name found) and was buried
at sea. In the late afternoon of February 19, 1906, they
arrived in Honolulu where local evangelic churches arranged a
large dinner reception and guest seats at the annual Honolulu
Rose Festival parade, but they would did not leave the ship.
The governor boarded the ship with 2 government
Russian-speakers to greet them and wish them well. One
translator was assigned to accompany them during their first
week. They proceeded directly to the northeast coast of Kauai
by evening, got a welcoming dinner and a train ride south to
the Makee Sugar Plantation, north of Kapaa at Kealia
Beach. Wagons took them to their own isolated work camp
of shacks, uphill from central Kapaa. Upon arriving, their
hosts found their shacks were vandalized by the vacated
Japanese workers who protested their own eviction and forced
job changes. (Exact location to be determined.)
The colonists immediately demanded and got many supplies,
food, bricks for ovens; divided into at least 2 religions, and
the Pryguny had 2 conflicting leaders. The parents of
the lost child wanted to go back. Upon learning they were
expected to cut sugar cane their first year, most refused to
work for $29 per month ($2 more than identical jobs at the
time). One man demanded $3.50 per day, the same wage he got in
California doing skilled factory work. On April 18, 1906, the
San Francisco earthquake occurred, one month after their
arrival.
Their homestead land and papers were approved in Washington,
DC, could not be prepared for months, per U.S. regulations,
and most wanted to buy communal land cheap rather than wait
for free homesteads. The land needed to be surveyed, parcels
marked and each homestead placed for access to water flowing
from the mountain. All did not want to live together and
seemed to have divided into 3 congregations. Different
plantations were scouted. The tropical weather and insects
were uncomfortable. Soon most wanted to return to Los Angeles.
Some were given jobs in Honolulu loading ships, others got
work on other plantations, on other islands, or building a dam
on Oahu. Within 5 months most had abandoned Hawaii. Slivkoff
was the most persistent and disappointed, and the last one to
leave on August 1, 1906, about 5½ months after he arrived.
On the way back by boat to San Francisco then by train to Los
Angeles, most Molokane and
some Pryguny chose
to stay in San Francisco. The first to arrive were taken by
wagon from the docks directly to the eastern side of Potrero
Hill to a refugee
camp, one of about 26
official
refugee camps. Men got jobs from the steamship company
that brought them from Hawaii, found work repairing earthquake
damage, and jobs at the nearby
factories. Most Molokane in Los Angeles joined
relatives and friends in San Francisco and Northern
California. Some moved to farms 25-50 miles eastward through
the delta,
close enough to bus in to San Francisco to attend a special sobraniya
over a weekend, while many met house to house.
Many who remained in "The
City" built or bought homes on "The Hill" and by 1928
several separate Molokan congregations united to build
a large meeting hall, the same year that the non-Molokan,
non-Dukhobor Spiritual Christians in Los Angeles published the
final version of their new Holy Book, Kniga solntse, dukh
i zhizn', and began to convert all in Southern
California to their new Dukh-i-zhiznik faiths.
The main Molokan prayer hall in America was built on
Carolina Street, San Francisco, near the top of Potrero Hill
in 1928, with a friendly Prygun congregation one
block away. 50 miles NE, rural Molokane met
house-to-house near Vacaville where
they used the Vacaville-El
Mira Cemetery. Later, a second Molokan prayer
hall was built east of Sheridan
(120 miles NE from San Francisco, 40 miles north of
Sacramento). Due to the large number of immigrants on Potrero
Hill, a local Presbyterian Christian women's club built a settlement
house on top of the hill in the midst of prayer halls of
4 non-Orthodox (Spiritual Christian) faiths from Russia (Baptist,
Evangelic, Molokan, Prygun). Later a Russian
Adventist congregation arrived.
To aid local immigrants, the Pastor of Olivet Presbyterian
Church at the NE edge of the hill (400 Missouri Street at
19th), opened his home and began offering English classes for
men in 1908. His work was similar to that of Dr. Rev. Barlett in Los Angeles, though
initially on a smaller scale, but with better management the
project grew and continues today. More classes were formed for
women and youth of all nationalities. In 1918, it was
incorporated as the "Neighborhood House" under the California
Synodical Society of Home Missions, an organization of
Presbyterian Church women. In 1919, renowned architect Julia
Morgan designed a permanent neighborhood house at 953 De
Haro Street. On June 11, 1922, the Potrero Hill
Neighborhood House was completed, mantled in beautiful
wood shingle and brick, with many broad windows and balconies
providing a panoramic view of San Francisco. A gymnasium was
added soon thereafter where Molokane and Pryguny hosted
basketball games with Dukh-i-zhizniki from Los Angles
in the 1950s.
In contrast to Spiritual Christians from Russia in Los Angeles
who lost their Bethlehem Institutes in 1914 and were forced to
move from The Flats(s) by urban renewal and highway building,
many families on Potrero Hill remained in place much longer.
The Molokan prayer hall never moved, but the Prygun
meeting house closed in the early 1960s when the man who
loaned the house died and the house was sold for $1000 at
auction for unpaid taxes.
Much more history to be posted about the actual, authentic,
real "Molokans in America."
8.
Folk Medicine
PAGE 45 But while these
attempts at colonization were occupying the minds of the elders,
the people in general were busy with their problems of making a
living, of bearing of children, arranging marriages, healing the
sick and burying the dead.
The age-old habit of healing the sick without the services of a
doctor continued in the midst of an abundance of doctors. The
services of their own "lekar" [doctor : лекарь], that it, old
man or woman skilled in reciting appropriate prayers for any
given disease, were thought to be sufficient for any occasion.
Doctors were called only in the last extremity. It was not until
the second generation Spiritual Christians
Molokans had their own families, that the
services of doctors became general.
In the matter of births too, it was thought that the services of
a doctor was needless and "high falutin'
". As long as several well-known and experienced midwives
were available just a short block away, why not use them? It was
a financial saving too.
The use of these "babkas" (elderly women) in place of doctors
was not entirely abandoned until the 1920's when the city health
authorities insisted that the midwives be licensed to practice,
and that they learn to write in order to be able to sign the
birth certificates as required by law. Being too old to learn to
write, they had to give up the practice but as long as they were
able to do so they unselfishly performed their functions at all
hours of the day and night, more often than not, without
remuneration [payment].
In 1907, the same year that Berokoffs
immigrated to Los Angeles, a charity maternity clinic was
opened at the corner of 1st and Rio streets in the Flat(s),
then moved and expanded as the "Maternity Cottage" to the
corner of 1st and Utah street, across from the future U.M.C.A.
and molodoi sobranie. The Maternity Cottage was funded
by several women's clubs, a business association, and an
internal second-hand baby-care store. The Cottage handled
more than 100 cases a year. School kids got free dental and
medical care from local hospitals. (Women
Appeal To Citizens To Raise $3000 Mortgage on P.-T. A.
Hospital, Parent-Teacher Edition, Los Angeles
Herald, May 21, 1912, page 14)
From 1915 to 1918, Home
Teacher Lillian Sokoloff taught immigrant mothers
homemaker skills, nutrition, medical-aid for children, how
to count and budget money — whatever was needed to navigate
and survive in the city.
Previous to this insistence of registering births, none were
registered; causing many persons thus unregistered needless
complications in securing their birth certificates when the need
for them became a necessity to get a job during the Second World
War. All born in the Maternity Cottage on
Utah Street across from the U.M.C.A. were registered.
This disregard or ignorance of the city and state laws in the
matter of vital statistics existed also in performing marriages.
It was not until ten years or more after coming to America that
PAGE 46 the required marriage licenses became general
at Prygun Molokan
weddings after the bride selling
scandal (1912-1915), arrests and fines in Arizona in
1920, and several court orders. During this same time period
various factions of Spiritual Christian Dukhobortsy in
Canada resisted registration of births, marriages, deaths, and
English schooling. (CITE)
An extensive list of folk medicine was
complied for Spiritual Christian Dukhobortsy by Dr.
Svetlana Inikova, with Koozma
J. Tarasoff: Volume
II. Doukhobor Incantations Through the Centuries.
(Ottawa: Legas Publishing & Spirit Wrestlers Associates,
1999, 137 pp.) See a short
promotional video by Tarasoff (1.5 min).
9.
Weddings — Also see: 5.
Bride-Selling Scandal above
But, the
weddings themselves were very joyful occasions. After all the
arrangements were made (at this time-1912—the boy and the girt
had a lot more to say about their future mates than when they
first came here) the trousseau prepared and guests invited,
came the day of the wedding. To begin the ceremony the whole
congregation as well as the relatives and friends of the groom
marched, singing in a procession in the middle of the street
from the groom's house to the home of the bride where part of
the ceremony was performed. After this the whole congregation,
augmented now by the relatives of the bride, reformed the
procession for the return march to the place where the
ceremony was to be completed. Since no meeting church
building of that time was large enough to accommodate such a
large gathering, it was frequently held in a tent temporarily
erected on the back yard of the groom's father or on the lot
of a friend or neighbor whose lot was roomy enough. Tents are
still used by Spiritual Christians in many villages in the
former Soviet Union.
After the ceremony was completed the newlyweds, together with
their invited friends, were seated in some large room adjacent
to the tent but separated from the congregation. There they
enjoyed their wedding dinner together with their invited boy
and girl friends, singing songs of their own choosing and
enjoying themselves in the traditional manner of young people,
while the congregation was enjoying their own dinner in the
tent.
The practice of marching in procession back and forth,
sometimes as far away as the Vignes Street area in Bethlehem
across the Los Angeles River First Street bridge to Utah
Street area in the Flats, continued until the police
authorities decided that, because of increasing street
traffic, it was becoming dangerous. They therefore requested
the elders to discontinue the practice and some time around
1915 the wedding processions were abandoned except for the
necessary relatives and friends who henceforth accompanied the
groom to the bride's PAGE 47 house and from
the bride's house directly to the site of the marriage
ceremony. Berokoff indicates that many still lived in the
Bethlehem district past 1915.
Of course the use of the automobiles
did not become general until the middle of the 1920's when
the Spiritual Christian Molokan population
scattered from the Flats to the various parts of east and
south Los Angeles.
10.
Funerals Also see Cemetery, Chapter 7
The funerals on the other hand, presented their own problems.
These were solved in the characteristic old Russia Molokan
fashion. Unlike present day funerals when all arrangements are
left to the undertakers, all work was done and all
arrangements were made by the family or by their relatives and
friends as they did in Russia.
Immediately upon the death of a person, the members of the
family bathed the body. If the deceased had been sick for a
while before death, all necessary clothing would have been
prepared before hand and the body would be dressed there and
then in the new apparel and laid out on benches in the front
room of the deceased's home. Meanwhile, friends and relatives
of the family skilled at carpentry would build a plain,
unadorned, redwood casket. A grave marker of 3x8 red wood
plank 8-ft. long would also be prepared. This would be
hand-carved with the necessary data prescribed by old
Russia Molokan customs A carryover tradition from their status as
heretics in Russia persists with their grave markers which
were forbidden to be in the shape of any cross, nor show any
Christian cross symbols.
Other friends would see to securing a burial permit and to
ordering a funeral car from the local streetcar company. They
would also order two or three regular streetcars to
accommodate the people for the trip to the cemetery.
But if the death was sudden, women friends would drop their
daily chores to sew the needed garments so that the body could
be bathed and dressed as soon as possible and placed in the
front room to be viewed and wept over. On the morning of the
funeral the body would be placed in the casket and everything
was ready for the funeral.
When the moment arrived for the funeral, the body was carried
out to the middle of the street where a rug was spread out. A
cloth-covered table was placed in the proper position PAGE 48 and the casket
was placed on benches near the foot of the table while the
proper hymn was sung for the rise and resurrection of the
deceased. After the usual prayers were recited, the body
accompanied by the singing congregation and the weeping
relatives and friends, was carried to the nearest streetcar
stop.
The casket would then be placed in the funeral car which
would also have room for the relatives while the rest of the
people would crowd into the specially ordered cars and,
following the hearse, would proceed to the place of
interment.
During the first five years
in Los Angeles the interment took place in the Los Angeles
County cemetery-for-the-indigent [called "Potters field"]
which was located (and still is*)
adjacent to the Evergreen Cemetery on East First St. But by
1909 the Molokan population increased
to such an extent that there was much grumbling among the
younger Maksimisty-Pryguny people
that our dead deserved a better fate than to be buried among
the county's indigent and undesirable elements** and that the Spiritual Christians from Russia Molokans
were now numerous enough to afford a cemetery of their own.
Consequently they began to agitate for the purchase of a site
for a private cemetery.
* In 1964, five years before Berokoff
published his book, the County sold 6 of its 10 acres to
Evergreen Cemetery and maintained about 4
acres with the crematorium.
** Most likely because they were
being buried among pork-eaters and pondering this Bible
passage from Matthew 27:7-10: "And after they had consulted together,
they bought with them the potter's field [Russian:
землею горшечника], to be a burying place for strangers.
... And they gave them unto the potter's field [Russian:
землю крови : field of blood], as the Lord appointed to
me." (Douay-Rheims Bible: Matthew 27:7-10)
But the urge to leave the city was so great that there was a
strong opposition on the part of the older generation who
argued that the Maksimisty Molokans were not
going to remain in the city very long,*
therefore a private cemetery was not needed. Despite this
opposition a half-acre site was purchased in 1909 on East
Second St. near Eastern Ave. This part of the city was
then an unpopulated barley field nearly a mile from the
nearest streetcar line. It was at the terminus of the Whittier
Blvd. car line near the intersection of Eastern Ave and up a steep unpaved road, which was often
muddy.
* 1907 prophesy that Maksim Rudoyotkin
will soon descend on Mt. Ararat with Jesus Christ. ("Modern Ways
Leave No Mark on Pryguny Molokanes,
Los Angeles Herald, April 21, 1907, page 3,
column 3)
In 1909 Orthodox Serbian immigrants had
bought a large tract of land east of Los Angeles for their Saint
Sava Serbian Orthodox Church of Los Angeles
(S.S.S.O.C.) and cemetery. Many of the younger Serbs thought
they had too much land and offered some to their Russian
Spiritual Christian acquaintances for their own cemetery.
The Slavs and Russians were often confused by outsiders, and
the press. They all spoke Slavic languages, were classmates
(English, citizenship, sloyd), neighbors and worked together
(factories, lumber, railway). By the 1950s, the Church
members wished they did not sell because they needed a
larger church which they built in San Gabriel in the early
1960s on donated land, maintaining the old Church for
smaller gatherings.
About the year 2000 the leaders of
S.S.S.O.C. proposed to their Dukh-i-zhiznik neighbors to
close off and annex the adjacent streets for a larger
parking area which both could use, which the Dukh-i-zhizniki
rejected. The unspoken likely reason for their rejection is
not that it was not a good idea which could benefit both
neighbors, but that the most zealous Dukh-i-zhizniki
believe they all will become Spiritually ne chistyi
(не чистый : unclean) because it is pohanyi (poganyi
: поганый : filthy) to have contact with pravoslavnye
(православные : Orthodox).
It's ironic that these Spiritual
Christians who complained of persecution by the Orthodox
Church in Russia and won't meet their neighbors half-way
today, accepted the generous offer 100 years ago from
friendly Orthodox Christians in the U.S. But, not all
American Maksimisty supported
those in L.A. being buried in land consecrated
by a priest, adjacent to and Orthodox church and
cemetery, especially with bodies traditionally buried facing
East, facing directly at an Orthodox cross on top of the
church. It is also a shame that they would not cooperate
like Christians with the mutually beneficial parking lot
proposal.
As soon as the site was purchased and fenced, permission was
secured from the County to remove all those bodies that were
buried in the County cemetery to the new location. In January and February 1910, 85 of 150
Russian Spiritual Christian graves (57%) Approximately
twenty or thirty bodies were
disinterred and PAGE 49
moved to the new site within a week with all due religious
ceremony and emotional expression from the bereaved families
who took advantage of the occasion to view their loved ones
for another and the last time.

For over a century, 65 Spiritual
Christians, born in Russia and
babies just-born in the US,
remain buried in unmarked graves along Lorena street under
the east end of Evergreen Cemetery. In 1910 they were left
behind in the former hillside "Potters Field," the Historic
Los Angeles Cemetery. In 1964, Evergreen Cemetery
bought most of this sloped land to expand, which was leveled
with fill dirt to sell graves on top of those buried 50+
years earlier. A common grave marker for these forgotten souls from Russia
should be properly placed there as the Chinese did for their
people in 2010,but it is nearly impossible to get local Dukh-i-zhizniki
to cooperate.
Although the distance from the end of the street car line to
the new cemetery was very long and up a
steep unpaved road, it did not deter the Spiritual Christians Molokans
from performing the full rites for the deceased as well as to
pay their last respects to them. The body was always carried
the full distance by relays of pallbearers, followed by the
full congregation singing the appropriate hymn the meanwhile.
This custom prevailed for a period of 12 years or until the
early 1920's when the motor driven hearse replaced the
streetcar and was able to deliver the casket to the gates of
the cemetery.
Henceforth every Spiritual Christian
Molokan
was assured of a burial plot. The Armenian Pryguny
Molokans too, were participants in the
undertaking and quite a number of their people were buried
there. Beginning in 1908, the Subbotniki choose
plots in the Jewish Home
of Peace Memorial Park on Whittier Blvd. Some who
intermarried with Pryguny
and Dukh-i-zhizniki
were buried in the new Slauson Ave cemetery.
But the half-hazard methods that prevailed in the purchase
and subdivision of the Guadalupe Valley Colony* and n Arizona
were employed here likewise. The plots
were neither surveyed nor numbered. No custodian was employed
until 15 years after the purchase and the nearest thing to a
manager was the keeper of the keys to the gate. Both Arizona and Mexico were the only
cemeteries which continued the old Russian tradition of dirt
mounds, though Arizona
adopted the concrete shell which defeated the need for a
mound.
* Berekoff did not know that there
were three
cemeteries in Mexico, also omitted in George
Mohoff's book, The
Russian Colony of Guadalupe Pryguny Molokans
in Mexico, 1995
Whenever a death occurred in the community, the family asked
for a half a dozen volunteers to dig the grave. These
volunteers would ask their foreman for two days off from work,
pick up the keys from the keeper and proceed to the cemetery
early in the morning by street car and set to work, first
selecting a plot that, in their opinion was appropriate. The
ground was so hard that with a pick and shovel it took the
half dozen men a day and a half to do the job. In recent decades an air-powered jack-hammer
chisel is used with air from a gasoline powered
air-compressor. In contrast the Slauson Ave cemetery
purchased in 1939 is on soft alluvial river silt.
It was a custom at the time to dig out a niche in the side of
the grave at its bottom, to protect the casket from the weight
PAGE 50 of the earth,
and also, if the deceased had a surviving spouse, to provide a
space easy to dig up for the
survivor upon his or her demise. This
custom is still practiced in many cemeteries in the Former
Soviet Union, and the entire hole is sometimes sprinkled
with white lime powder, if available, for appearance and to
disinfect the soil.
This half-hazard method of selecting a plot later caused some
unpleasant complications. In time the cemetery became over
crowded and the diggers, acceding to the wishes of the
bereaved family, started to dig out the niche unaware that
there was already a niche from the neighboring grave
containing a casket. Of course they would immediately abandon
the attempt; nevertheless, the relatives of the person whose
grave had thus been disturbed, were sometimes bitter in their
complaints. Initially there was no
system for surveying, measuring and numbering grave plots,
until required by law. Burial permits must specify the exact
location of burial.
After WW2, Dukh-i-zhizniki in
Southern California performed a modernized traditional
old-world Russian funeral with an open casket. Depending on
the family, congregation and type of death, the body may
still be prepared and dressed at home not embalmed, but as
with home births, more people gave into the funeral industry
and paid for chose not to do the gruesome task likely
embalmed at a mortuary.
The most zealous were against embalming
because they believed one could not resurrect from the dead
and ascend to heaven if any essential body parts were
missing. Some allowed embalming if all the blood drained was
saved in jars to be placed in the casket during burial, not
knowing that families were given only a few quarts of the
several gallons of total embalming wash used. In
Arizona, the elder immigrant John "cheese" Tolmachoff had
diabetes, and his gangrene leg was amputated. The family
kept the leg in their home freezer and placed it in the
casket before burial.
When the body is placed in the casket a
prayer is recited, usually by the presbyter or lead elder of
the congregation that will host the funeral, and the casket
is transported to a viewing location in a rented hearse, or
private van. In Russia the casket was carried to the village
cemetery, in America they began to use vehicles.
Depending on the congregation and
family, the open casket may be viewed at a mortuary, private
home, or congregation meeting hall. Wreaths of flowers may
be donated and placed in the room. Russian songs of mourning
are sung, for hours, and longer depending on the stature of
the deceased person and number of people attending. Some
songs may be loud, with jumping, raising of hands, and
shouts in Russian. Prophesies may be delivered. Several
congregations believe by tradition that a casket is
"unclean" and do not allow it to be viewed in their main
meeting hall, so some have a side building used for
funerals. The casket is viewed by family and guests during
an evening service, and (depending on the family) the open
casket may be watched all night, or closed until morning.
Food is provided in the meeting hall kitchen particularly
for out of town guests.
On burial day, after evening viewing,
everyone arrives for a morning service, which ends to allow
time to move the casket to the cemetery for a prearranged
announced burial time. Before the casket is moved from the
viewing location ritual prayers are recited and songs sung
as family and friends are invited to kneel before the
casket. Dukh-i-zhizniki have specific prayers and
songs used by no other family of faiths, some of which vary
depending on how esteemed and holy the deceased was to those
gathered. Then the open casket can be move out of the
building onto the street to a vehicle by pall-bearers. On
the street another ritual prayer with song is performed
before the open casket is closed and transported to the
cemetery, sometimes with wreaths of flowers on top.
At the cemetery, the casket is opened
upon removal from the vehicle and carried or rolled by cart
to the grave site with any flowers accompanied by singing.
Depending on the space available and weather, people
typically line up in formation with men and women separated,
in rows, face-to-face, or as they arrange for Sunday service
with women at one end perpendicular to two rows of men
facing each other. The deceased family is on one side of the
grave, and the presbyter and attendees on the other side.
The casket is placed on support boards over the grave, and
remains open for a final prayer. Singing continues as
volunteers place the lid on the casket. Two straps are
placed under the casket and 4 men raise it so the support
boards can be removed, and slowly lower the casket to the
bottom. The straps are removed, and cement protection blocks
are placed over the casket. Fresh
dirt on a shovel is passed around for those who wish to
throw a handful into the grave. No flowers are tossed into
the grave.
Singing continues as volunteers take
turns shoveling dirt into the grave, until full. In recent
decades, depending on the cemetery, they fill the grave half
full, to be later compacted, filled, and compacted again.
After burial, singing stops and a male
representative of the deceased family moves to the center of
the gathering to announce in Russian. All are thanked for
coming and invited to the hosting meeting hall, or other
place, for a short service and meal to begin in a few hours
and last 2 to 4 hours. This give all a chance to go home, to
their hotel, bathe, rest and change clothes. The change of
clothes is important for Dukh-i-zhizniki who believe
that a dead body is unclean and so are they for being in the
same room with the casket.
If the deceased is a long term high
ranking member of the congregation, preparations for the
meal began at death and a small team of cooks ordered and
prepared a 4-course feast, typical for Spiritual Christian
funerals. The cooks will start early in the morning many
missing the burial. Divorced people, or assimilated families
whose members rarely attended service will avoid a large
traditional feast and its expense by inviting people to
their house, and in some cases to a rented catering hall. In
any case, having a meal gathering after a funeral is
tradition. Some dysfunctional families refuse to cooperate
and avoid a meal.
[map and list of cemeteries]
<Chapter 1 — Contents — Chapter 3>
Spiritual
Christian History
Spiritual Christians
Around the World
 PAGE 32 The city of
Los Angeles was chosen, instead
of Canada, for
PAGE 32 The city of
Los Angeles was chosen, instead
of Canada, for 






